For 2D materials that are only made up of a few layers, when it comes to tuning physical properties, stacking configuration can provide a crucial sense of freedom. For instance, trilayer graphene possesses two stable stacking sequences, ABC and ABA, as displayed in Figure 1.
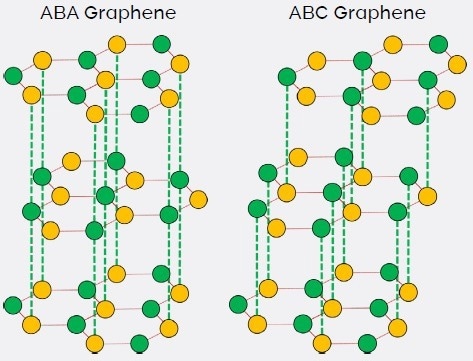
Figure 1. Lattice structure of ABA graphene (left) and ABC graphene (right). Image Credit: Asylum Research - An Oxford Instruments Company
In the ABA (Bernal) polytype, three individual graphene sheets possess mirror symmetry, producing a band overlap that expresses semimetallic properties. Conversely, there is a lack of mirror symmetry in ABC (rhombohedral) stacking, which is a semiconductor with a gate-tunable bandgap.
The ABC structure is marginally less stable than the ABA structure and, therefore, not as commonly found on trilayer graphene.
It can be prepared either by exfoliation, which involves stacking a monolayer of graphene on a bilayer with a small twist angle or by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on a curved substrate.1
The novel properties of ABC graphene have garnered considerable attention in research applications. Superconductivity,2 insulating behavior,3 and ferromagnetism4 have all been observed on ABC graphene structures.
References
- Gao, Z. et al. (2020) Large-area epitaxial growth of curvature-stabilized ABC trilayer graphene. Nature Communications 11, p. 546.
- Chen, G. et al. (2019) Signatures of tunable superconductivity in a trilayer graphene moiré superlattice. Nature 572, pp. 215–219.
- Chen, G. et al. (2019) Evidence of a gate-tunable Mott insulator in a trilayer graphene moiré superlattice. Nature Physics 15, pp. 237–241.
- Chen, G. et al. (2020) Tunable correlated Chern insulator and ferromagnetism in a moiré superlattice. Nature 579, pp. 56–61.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Asylum Research - An Oxford Instruments Company.
For more information on this source, please visit Asylum Research - An Oxford Instruments Company.