Renishaw’s Empty Modelling method is available within its Windows®-based Raman Environment™ (WiRE) control and analysis software. The software’s patented algorithm is able to derive pure and identifiable component spectra from intricate mixtures of measured data, even in instances where users have no prior knowledge of any potentially present species.
The Empty Modelling method is able to identify chemical species present in a matter of seconds, extracting these from millions of spectra and generating chemical images of their distribution. This method is even suitable for use in applications where individual spectra are representative of mixed components.
This method employs multivariate analysis, and this analysis is based on the whole spectrum rather than the intensity of a single Raman band. This approach yields accurate results which can be linked to real chemical properties directly.
The Empty Modelling method can be run unsupervised, meaning that there is no need for users to guide the software or input a list of suspected species. The software will objectively analyze the dataset, providing users with clear results.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
PCA has traditionally been the method of choice when analyzing complex datasets with no available reference spectra. PCA works by determining variance in the data, extracting components or ‘loadings’ based on their significance. These abstract loadings are more difficult to interpret than Raman spectra, however (Figure 1A).
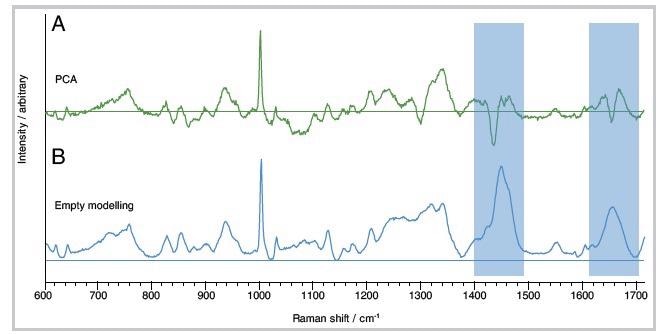
Figure 1. Protein component spectra obtained from a sample of porcine tissue. (A) Biological loading obtained from PCA. The spectrum is an abstract mathematical representation of the data – as indicated by negative peaks. (B) Biological component obtained from the Empty Modelling method. The spectrum represents a real material. Image Credit: Renishaw plc - Spectroscopy
How the Empty Modelling Method Works
The Empty Modelling method’s algorithm is fully unsupervised and is based on multivariate curve resolution alternating least squares (MCR-ALS). The algorithm iteratively breaks the spectrum down into its the key components, continually optimizing the fit as it does this.
With PCA, however, the concentration and features of each loading’s are constrained to be positive, allowing it to better resemble a genuine Raman spectrum (Figure 1B). Because of this, users can quickly and easily identify key chemical components from Raman mapping data that is complex and non-homogeneous.
The Empty Modelling method functions iteratively, continuing to improve components’ spectra as they are extracted from the data and ensuring that the sample’s chemistry is as accurately matched as possible.
The process may be halted when a pre-determined percentage of the variance in the data has been explained, or once a set target number of components have been identified.
Easy Analysis
Once analysis is complete, the user is presented with a simple view of the components present (Figure 2), and when a specific component is selected, the system will display that component’s spectrum as well as its distribution within the sample. The user is then able to click points on the map and compare single map spectra with the component spectrum, making reviewing the data straightforward.
The user is also able to directly identify components by using the Spectrum Search module to search the wide range of spectral libraries available from Renishaw.
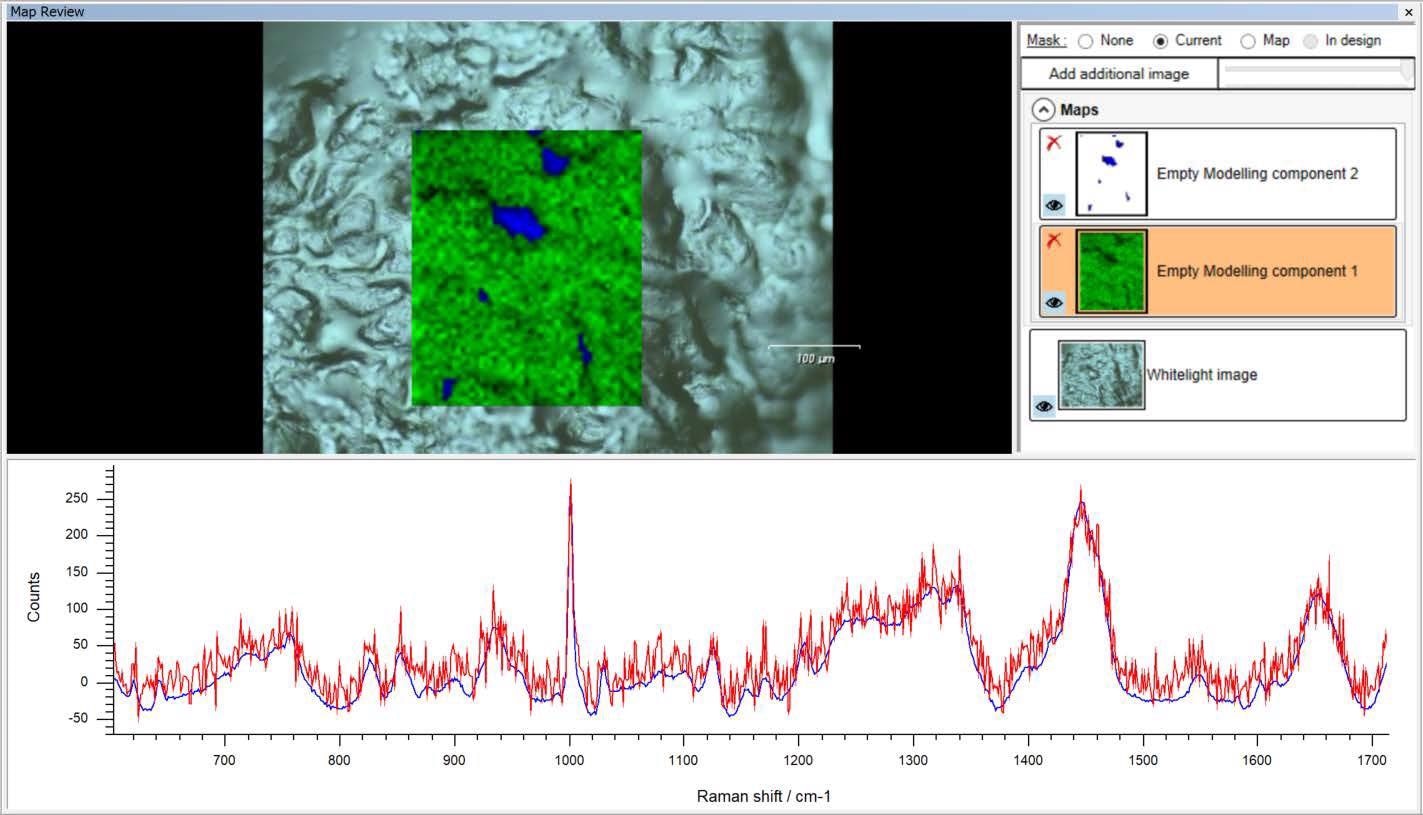
Figure 2. After analysis, the Empty Modelling method displays the component spectra and the corresponding concentration images. Image Credit: Renishaw plc - Spectroscopy
Easy Interpretation
Unlike conventional unsupervised analysis techniques, the Empty Modelling method’s component spectra relate directly to genuine Raman spectra. Because of this, it is comparatively easy to characterize unknown materials and identify components within large Raman data sets.
Simplified Sample Analysis
The Empty Modelling method is rapid, providing results that are easy to interpret while working seamlessly with the WiRE Raman control and analysis software from Renishaw.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Renishaw plc - Spectroscopy.
For more information on this source, please visit Renishaw plc - Spectroscopy.