Manufacturing Electrodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries charge and discharge because their lithium ions can move in both directions between positive and negative electrodes. Lithium-ion batteries have generally been used in a compact form, such as in mobile phones, computers, and digital cameras, but there is a growing demand for lithium-ion batteries with an electric capacity large enough for electric vehicles (EVs).

Positive electrode (left), negative electrode (right).
Manufacturing an electrode for lithium-ion batteries involves three basic steps:
- Apply an electrode slurry material to a metal foil sheet called a collector
- When the electrode slurry is dry, press the sheet
- Use a cutter or slitter to cut the sheet into pieces of a specified size
It is critical the electrode material on the sheet has the appropriate surface roughness to adhere securely to the separator. Inspectors must use a roughness measuring instrument to check the surface roughness of lithium-ion battery electrodes.
Various surface roughness measuring instruments are available, but many lack the precise measurement capabilities needed for this application. For instance, contact-type roughness gages can sometimes damage the electrode surface, while interferometers are unreliable because the black electrodes absorb the light they use for measurement.
In contrast, laser scanning microscopes like the Evident LEXT™ OLS5000 system can precisely and nondestructively measure the roughness of electrodes.
Precisely Measure the Roughness of Large Electrodes Using the LEXT OLS5000 Microscope
The noncontact measurement of the LEXT OLS5000 3D laser scanning microscope is well-suited for measuring the surface roughness of large electrodes for several reasons:
- The noncontact measurement method eliminates the risk of damaging the electrodes as well as collateral data errors
- Although electrodes are black and have a very low light reflectivity, only a minute amount of reflected light is needed to obtain the required data
- Using an optical system unique to laser microscopes, the LEXT OLS5000 microscope enables the user to acquire data that is accurate to the center of the field of view and the surrounding area
- Various types of data can be stitched horizontally, enabling users to acquire surface roughness data over a wide area
- The LEXT OLS5000 system enables users to simultaneously observe the 3D images, pseudo color, and height information from a laser microscope and the real color images from an optical microscope. This means inspectors can combine the numerical roughness data with their observations of the electrode texture to better understand the state of the electrode’s surface.
Example Images
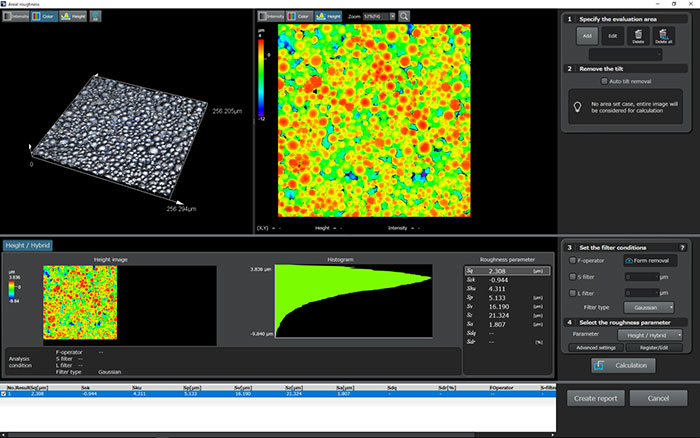
Example of roughness measurement of a positive electrode.
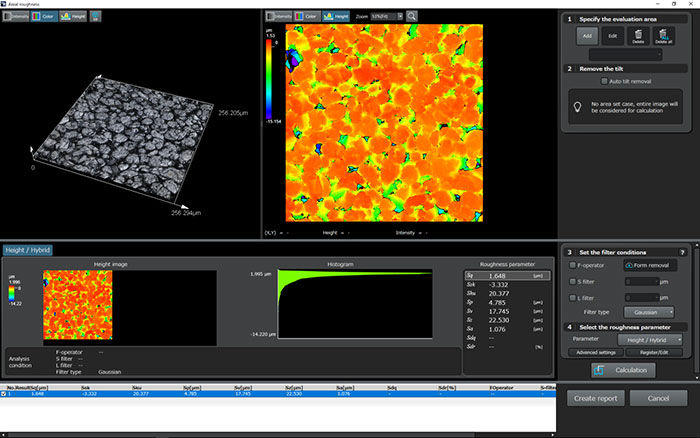
Example of roughness measurement of a negative electrode.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Evident Corporation - Industrial Microscopy.
For more information on this source, please visit Evident Corporation - Industrial Microscopy.