New product development (NPD) teams are constantly searching for a competitive advantage that will allow them to create electronic devices that are smaller, appliances that are more reliable, vehicles that are safer, or instruments that are increasingly precise.
This range of products frequently requires highly engineered metal components on an increasingly miniaturized scale, and the demand for these miniature and micro metal components is increasing. Businesses developing these products have a range of choices in sourcing these components, looking to meet critical functional specifications without compromise to design for manufacture (DFM), design for assembly (DFA), quality and cost.
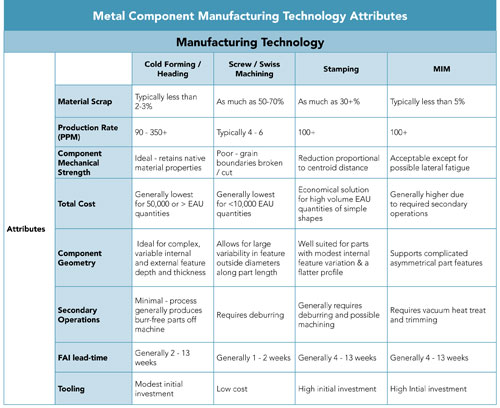
Comparing the available processes to one another in accordance with cost-benefit criteria by which they are usually assessed brings to the forefront one method that is frequently overlooked.
Cold forging, or cold forming, is when force is applied with a punch to a metal blank staged in a die. The force surpasses the elastic limit of the alloy, leading to plastic flow until the metal blank forms the shape bound by the punch and the die. As implied by the name, this process of forming is accomplished through force alone, without the application of added heat or cutting and shearing.
The benefits and drawbacks are highlighted in the table below, along with three examples of cold forged components. It has also been discussed why it is that cold forming is so frequently overlooked when searching for a component producer.
Product Development Concerns Regarding Micro Component Manufacturing Processes
Source: Sussex Wire
Cold Formed Component Examples
Glass to Metal Seal with Terminal Flattened and a Pierced Oval Hole

Image Credit: Sussex Wire
Usage: Terminal component in high volume glass to metal seal (hermetic) electronics devices.
Material: Expansion Alloy - 52 alloy (nickel/iron alloy) per ASTM F-30 glass-to-metal seal quality.
Manufacturing Process: Formed and pierced using a slide machine. Complete off machine.
Noteworthy Features:
- Great surface finish on the sealing surfaces and there are no leak paths.
- Hole, or oval, diameter is centered within terminal flat area.
- Hole diameter held to +/- .002" (+/- .05 mm).
- Flat end is trimmed perpendicular to lead axis.
Benefits:
- Minimal material waste.
- Elimination of the presence of spiral machining lines through cold forming the pin.
- High production speeds allow for low manufacture costs on high volume production runs. It is much quicker than machining and there is much less material cost compared to machining.
Ceramic Surge Protector Component

Image Credit: Sussex Wire
Usage: Mounting surface/heat sink for diode chip.
Material: CDA 102 oxygen free copper/conductivity is high.
Manufacturing Process:
- Multi die cold formed.
- Produced as a complete part on proprietary manufacturer designed and built cold form tooling.
Noteworthy Features:
- Micro dimples (.010", .3 mm) on minor OD.
- Pedestal edges have sharp corners.
- Finish is smooth on .040" diameter surface (die mount surface).
- Note: one end has a precise chamfer.
Benefits:
- Formed from wire, no machining required.
- High manufacture speeds allow for low production costs and is much quicker than machining or turning.
Stainless Steel Eyelet

Image Credit: Sussex Wire
Usage: Glass to metal seal body used in airbag igniters.
Manufacturing Process:
- Multi die cold formed.
- Produced as a complete part on proprietary designed and built cold form tooling.
Noteworthy Features:
- Double Diameter OD major and minor ODs.
- Center hole is a through hole and surface finish is high.
Benefits:
- Formed from wire with minor (planned) scrap.
- High manufacture speeds that allow for low production costs and make it much quicker than machining or grinding.
- The inside diameter is punched, so there are no spiral drill lines that would form a leak path.
- Flat top surface with a good surface finish for wire bonding.
- Inexpensive cold formed rectangular feature which is much more efficient compared to machining.
- Material is suitable for welding (low carbon content).
Bringing Cold Forging in From the Cold
The question being asked is if cold forging is so successful, why is it not being used by everyone?
Industrial and manufacturing engineering programs in Academia include design for machining as a relatively standard undergraduate necessity, but cold forging is seldom spoken about. There are limited universities offering advanced coursework in design for cold forging in comparison to the high number of programs of study offering design for injection molding, stamping, and machining.
Outside of academic settings, commercial training programs are also limited in offering much in the way of cold forming training. Micro-component producers offering cold forming is rare, along with manufacturers offering the necessary design training, so in order to maintain proficiency in cold forging methods, a large proportion of the commercial training in cold forging needs to be provided by the producers of the cold forge equipment themselves. However, the majority of this training is aimed at the purchasers of the cold forge machinery, and not the product engineers.
As a consequence, new product development teams are using the tools they are familiar with, and seldom do individuals on the team have experience with design for cold forging as a tool. As a result, for cold forging companies to succeed in an industry of engineers that are not familiar with their process, they need to offer fully vertically integrated service, providing knowledge of each step of producing a part that meets customer specifications.
New product development teams can expect much more than just a contract component manufacturer, but also collaboration on all levels of the component development, from material election, to design, to prototype, to manufacture. Sussex Wire can help companies gain the competitive edge without compromising quality.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Sussex Wire Inc.
For more information on this source, please visit Sussex Wire Inc.