Li-ion batteries are power sources of many electronic devices that are used in daily life, for example, laptops, cellphones, car batteries, etc. These complex energy-storage devices can contain many different materials including metals and polymers. These types of batteries have polymer binders that are delicate beam-sensitive structures which can easily get damaged when scanned with a high-energy electron beam probe. This fact can make SEM imaging of these samples very difficult.
This poses a major challenge since the observation of the internal structure of electrodes of these batteries is very important for battery producers. This is due to the fact that the internal structure of the electrodes of Li-ion batteries varies during their lifetime and such changes have considerable effects on the performance and final quality of the batteries. It is important to understand these changing processes to overcome performance problems and design better energy-storage solutions.
TESCAN S8000G FIB-SEM
An ideal solution to satisfy the analytical and imaging requirements in the battery industry is the new TESCAN S8000G FIB-SEM system. On one hand, the S8000G microscope includes the new BrightBeam™ SEM column capable of field-free ultra-high resolution (UHR) imaging and is fitted with a robust detection system. The BrightBeam™ SEM column offers enhanced resolution particularly at low electron beam energies which makes it perfect for imaging both non-conductive samples and beam-sensitive specimens (for example, the binder materials) at energies that can be as low as just a few hundreds of eVs without affecting image quality.
The detection system, in turn, is made up of an in-lens detection system with angle-selective electron signal and energy-filtering capabilities, thus allowing a range of image contrast varying from topographic to compositional with a clear discrimination of BSE and SE signals. Electron signal separation based on user-defined energy-filtering windows allows tunable surface sensitivity which can offer unique BSE material contrast of binder materials with no damage, and maximum information of the uppermost surface layers of the sample by choosing BSEs within a narrow range of energy. It is possible to obtain different signals simultaneously, thereby maximizing information and insight into the nanostructure of lithium batteries, see Figures 1 and 2. The energy-filtering capability can also be used for lowering charging artifacts during imaging.
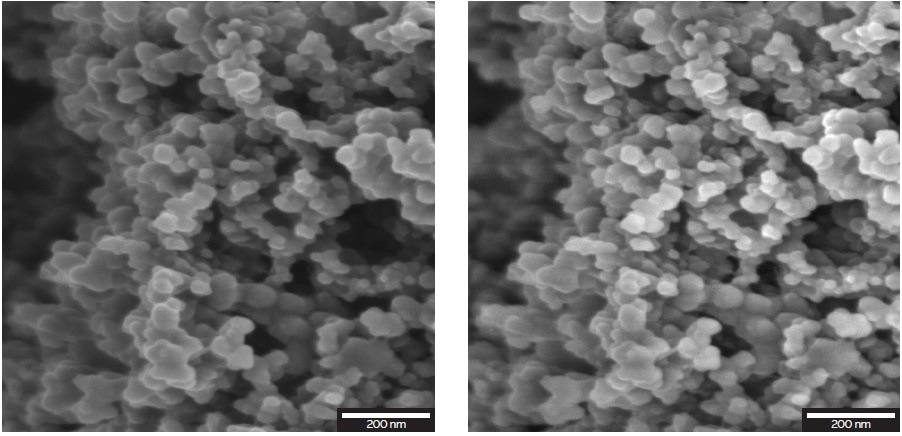
Figure 1. Nanostructures of a Li cathode observed with the Multidetector (left) and the Axial detector (right) imaged at 2 keV.

Figure 2. Cathode of a Li-ion battery imaged at 2 keV with the E-T detector (left), and, with the Multidetector with the energy-filtering grid OFF for detecting SE signal (center) and ON for detecting BSE signal (right).
On the other hand, with regards to sample modification, the TESCAN S8000G FIB-SEM system is fitted with the novel Orage™ Ga FIB column with enhanced ion optics for excellent low-energy beam performance, better resolution, and high ion beam currents up to 100 nA for maximum throughput and excellent results. These features enable the preparation of cross-sections (Figure 3), high-quality damage-free TEM specimens, and FIB-SEM tomography for examining the microstructure of electrodes of Li-ion batteries at different cycles that gives a better understanding of the internal structural changes that take place during these processes.

Figure 3. 50 μm long cross-section prepared with new Orage™ Ga FIB column and imaged at 2 keV with E-T detector (left), Axial detector (centre) and Multidetector (right).
TESCAN Group
Founded in 1991 by a group of managers and engineers from Tesla with its electron microscopy history starting in the 1950’s, today TESCAN is a globally renowned supplier of Focused Ion Beam workstations, Scanning Electron Microscopes and Optical Microscopes. TESCAN’s innovative solutions and collaborative nature with its customers have won it a leading position in the world of nano- and microtechnology. The company is proud to participate in premier research projects with prominent institutions across a range of scientific fields. TESCAN provides its clients with leading-class products in terms of value, quality and reliability. TESCAN Group is the North American arm of TESCAN Group, a multinational company established by the merger of Czech company TESCAN, a leading global supplier of SEMs and Focused Ion Beam workstations, and the French company ORSAY PHYSICS, a world leader in customized Focused Ion Beam and Electron Beam technology.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by TESCAN Group.
For more information on this source, please visit TESCAN Group.