As the acronym suggests XPS (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy) is a spectroscopic technique. An XPS spectrum is displayed as the number of photoelectrons collected by the detector as a function of their energy, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: XPS survey spectrum of SiO2 passivation layer on Si elemental substrate. Credit: Kratos Analytical
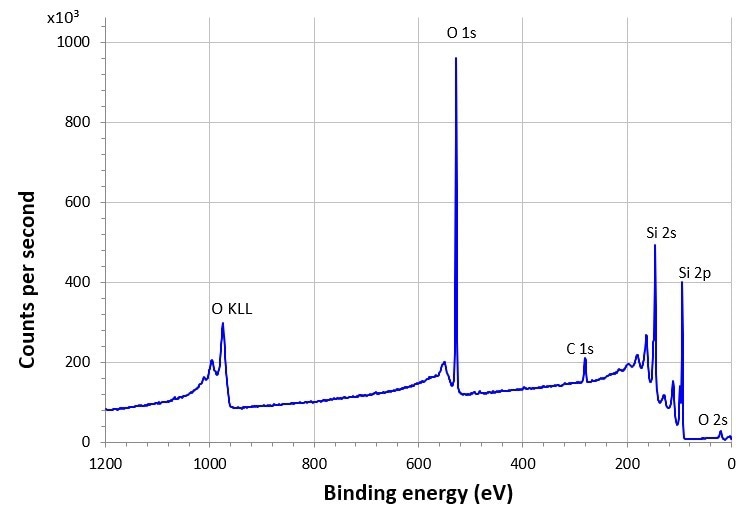
The technique is relatively simple, involving the irradiation of the sample by X-rays and collection of the ejected photoelectrons. The spectrometer is designed to collect as many of these photoelectrons as possible. The efficiency of the photoelectron collection is referred to the sensitivity of the instrument and is expressed as the counts per second, usually of a peak after the background of inelastically scattered photoelectrons has been subtracted. To allow comparison of the performance of X-ray photoelectron spectrometers to be compared, most manufacturers quote the sensitivity of their instrument using the silver 3d5/2 peak.
The area under a photoelectron peak is directly proportional to the number of atoms of that element within the sampled volume. This means that XPS is a quantitative technique. It can provide the relative atomic concentration of the elements present within the material.
The sensitivity of a spectrometer will largely determine the ability to detect the elements present. It should be recognized that different elements and indeed different electronic core-levels within an element will have different probabilities of ejecting a photoelectron. It is necessary to account for this physical property when quantifying XPS spectra with a term known as the relative sensitivity factor (RSF).
The number of photoelectrons ejected from the sample will also be affected by instrumental settings. Increasing the fluence of incident X-rays will increase the number of ejected photoelectrons. However, this approach can also lead to unwanted X-ray-induced sample degradation. A much better approach is to collect as many of the photoelectrons generated as possible. This is achieved by innovative electron optics such as the magnetic immersion lens and aberration-corrected input lens. A large radius hemispherical analyzer also ensures high transmission of the photoelectrons to the detector.
However, the sensitivity only defines part of the spectrometer’s performance. As XPS is a spectroscopic technique the energy resolution of the instrument is also of fundamental importance. The ability to accurately measure the small changes in energy, or chemical shifts, of the core level peaks is necessary to determine the chemical environment of the elements probed. The energy resolution of an XPS instrument is usually defined as the full width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the Ag 3d5/2 peak. A state-of-the-art spectrometer will be capable of an energy resolution of < 0.45 eV FWHM on the Ag 3d5/2 peak.
Figure 2: synthetic core level peaks with an intensity ratio of 5:1 and energy separation of 1.5 eV. (A) peak FWHM = 0.48 eV and (B) peak FWHM = 1.0 eV. Credit: Kratos Analytical
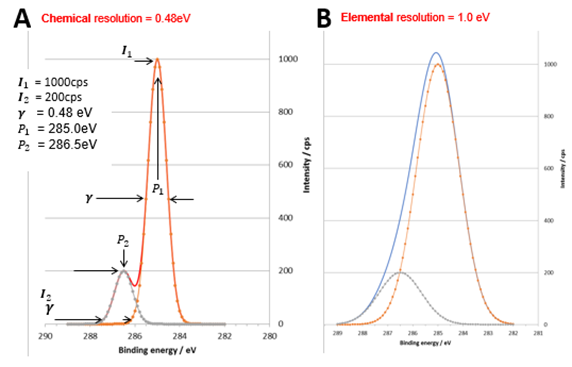
The importance of energy resolution is demonstrated in figures 2(A) and (B) where two symmetrical peaks with an intensity ratio 5:1 are separated by 1.5 eV. In figure A the energy resolution γ = 0.48 eV. The summed spectral envelope shows a clear dip between the two components, allowing unambiguous identification of each component. In figure B, the energy resolution is degraded to γ = 1.0 eV. It is no longer possible to resolve the two components. Identification of the two chemical states for a narrow region spectrum measured at this resolution is ambiguous.
As suggested by the title of this article, both the sensitivity and the energy resolution are important parameters in defining the overall performance of the spectrometer. The two terms are inversely dependent on each other. As the energy resolution of the spectrometer increases (narrower peaks, better energy resolution), the sensitivity decreases (lower counts per second, noisier spectra). An understanding of this principle is important when defining acquisition parameters for a spectrum. If the information that is required is simply the elemental composition, then a fast, low-resolution survey spectrum acquired with high sensitivity will provide the result. Conversely, if a detailed understanding of the chemical state is required, a longer acquisition at higher energy resolution will allow the peak positions of the peaks to be identified.
The relationship between sensitivity and energy resolution is also important when comparing the performance of different spectrometers. Ultimate spectral energy resolution < 0.45 eV of the Ag 3d5/2 component is of little practical use if the sensitivity is so low that a spectrum with acceptable signal-to-noise takes 30 minutes to acquire an acceptable signal-to-noise ratio.
Figure 3: Large analysis area performance of the AXIS Supra+. Sensitivity (cps) of the Ag 3d5/2 peak as a function of resolution (FWHM). Credit: Kratos Analytical
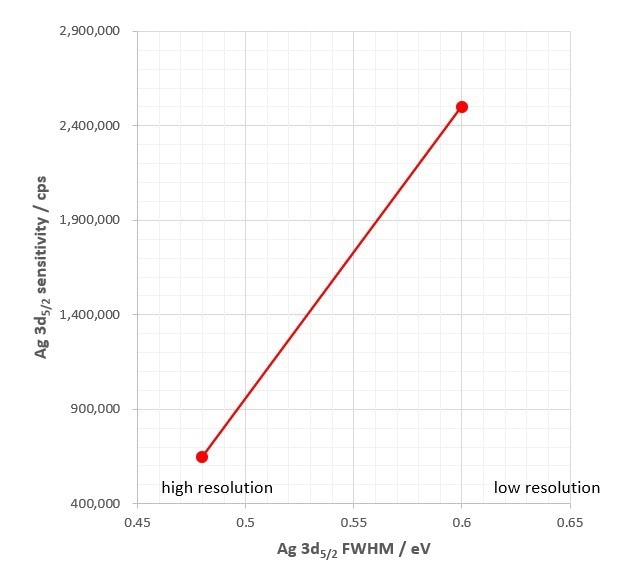
The best X-ray photoelectron spectrometers will combine excellent sensitivity AND energy resolution, as demonstrated by the large analysis area specifications for the AXIS Supra+ in figure 3, which sets the benchmark for a modern XPS instrument.
Learn more about the AXIS Supra+