Organic acids found in fruit juices include citric, malic, lactic, tartaric, and acetic acids, which are either naturally occurring or added artificially. There are also several inorganic acids, such as phosphoric and carbonic acid.
The acids present indicate the degree of ripeness. Their influence has an impact on the flavor (tartness), color, stability (shelf life), and quality level. They also help in slowing microbial growth.
Apart from impacting quality and shelf life, acidity is an important consideration for consumers as it can cause dental erosion, acid reflux, and more. As a result, it is necessary to detect the acid level in juices and beverages. Titration is an effective method for determining the acid content or total titratable acidity of these goods.

Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Discussion
This process uses titration with sodium hydroxide to determine the acid level of fruit beverages (juices and pulp). The titration is monitored by potentiometric measurement using a pH sensor and ends at a predetermined pH, known as the endpoint (EP).
Sample
- Orange and Pineapple Juice: five to 10 g
- Orange juice concentrate: one to five g
Preparation Procedure
- Calibrate the pH sensor using METTLER TOLEDO buffer solutions at pH 4.01 and 9.21.
- Determine the titer of the titrant using 0.07-0.12 g of potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) as the principal reference.
- Begin the titration by weighing the sample and adding 50 mL of deionized water.
Chemistry
H3C6H5O7 + 3NaOH → Na3C6H5O7 + 3H2O
Compound
- Citric acid, M = 192.124 g/mol; z = 3
Chemicals
- Deionized water
- MT Technical buffers for calibration of pH sensors (pH 4.01 and 9.21)
Titrant
- Sodium hydroxide, NaOH, c(NaOH) =0.1 mol/L
Instruments and Accessories
- EasyPlus Titrator Easy pH (30060041) or Easy Pro (30060044)
- pH sensor, EG11-BNC (30043103)
- EasyPlus Burette 10 mL (30043901)
- Magnetic Stirrer bar (51191159)
- EasyDirect™ titration software (30065449)
- Titration beakers PP 100 mL (101974)
Method
Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| . |
. |
| EQP /EP |
EP |
| Titration type |
Direct |
| Sample ID |
Juice |
| Prestir duration |
20 s |
| Sample size entry |
Variable weight |
| Multiple determination |
Yes |
| Endpoint value |
8.2 pH |
| Control |
Very cautious |
| Stir |
High |
| Predispense |
0 mL |
| Calculation |
Content [g/L]; [%] |
| Report |
long |
Results
Citric acid content in various beverages: juice/concentrate (n=5). Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
|
Juices |
Orange juice concentrate |
|
Orange [g/L] |
Pineapple [g/L] |
[%] |
| 1 |
5.17 |
5.08 |
2.50 |
| 2 |
5.17 |
5.09 |
2.48 |
| 3 |
5.17 |
5.08 |
2.49 |
| 4 |
5.16 |
5.09 |
2.48 |
| 5 |
5.16 |
5.07 |
2.48 |
| Mean |
5.16 |
5.08 |
2.48 |
| s |
0.004 |
0.008 |
0.009 |
| srel [%] |
0.10 |
0.16 |
0.40 |
Titration Curve
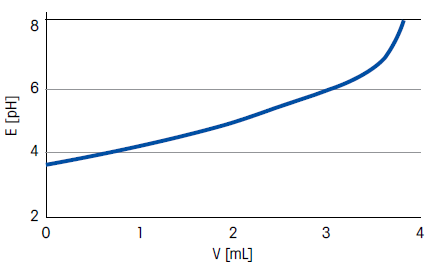
Figure 1. Titration curve for orange juice. Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Waste Disposal and Safety Measures
Once complete, neutralize the solution before disposing of the final solution.
Remarks
- Density should be used when making calculations where the results are provided in 'g/L' and the sample size is in 'g'.
- The sensor should be washed fully after each analysis.
- Calibrate sensors on a regular basis.
- Protect NaOH from ambient CO2 with Ascarite (II) adsorbent.
- Measure juice concentrates using this method. Depending on the acidity of the aqueous solution, NaOH at a greater concentration (e.g., 0.5 mol/L) may be used.
- Use a fresh sample for analysis.

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Mettler-Toledo - Titration.
For more information on this source, please visit Mettler-Toledo - Titration.