In today's fast-changing chemicals industry, the ability to respond quickly and accurately to consumer demands separates market leaders from followers.
As brands want more sustainable, bio-based alternatives without sacrificing performance, technical service teams are under pressure to deliver creative solutions faster than ever before.
Traditional formulation development techniques, which include time-consuming iterative testing, prolonged stability studies, and trial-and-error experimentation, are no longer sufficient to meet market demand.
This article investigates how artificial intelligence is radically changing the formulation development landscape, enabling chemical suppliers to achieve unprecedented levels of client response while reducing development costs and speeding time-to-market.
Companies can now generate reusable predictive assets using platform-based AI modeling, allowing technical service teams to quickly analyze formulation options, forecast performance results, and reliably offer optimum solutions to clients in days rather than months.
Application Models: Creating Reusable AI Assets for Customer Success
The paradigm change offered by AI-driven formulation platforms is based on a single concept: translating experimental data and domain expertise into reusable prediction models that can be quickly deployed across numerous client situations.
Unlike typical one-time development projects, in which knowledge is compartmentalized in lab notebooks and individual scientists' experiences, application models become organizational assets that grow in value with each use and can be utilized across the team.
Creating an Application Model
- Build the Foundation: Establish the foundation by organizing and storing historical trial data, ingredient qualities, and process parameters in a central platform.
- Train Predictive Models: Machine learning algorithms can detect patterns and correlations between formulation inputs and performance outputs.
- Define Search Spaces: Limiting materials, concentrations, and processing parameters ensures recommendations are commercially viable.
- Deploy for Customer Response: Technical service teams use application models to quickly analyze ingredients and make data-driven recommendations.
Deploying An Application Model
This strategy changes the economics of client technical service. Models produced for a single customer project are immediately applicable to subsequent requests.
When another customer comes in with comparable but distinct needs, technical teams may simply tweak the targets and constraints within the existing model framework, delivering new suggestions in hours rather than starting from scratch.
This reusability has a multiplicative effect on ROI, since each model gains value with each subsequent use.
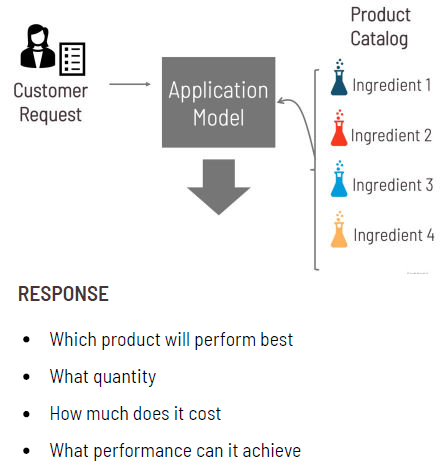
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
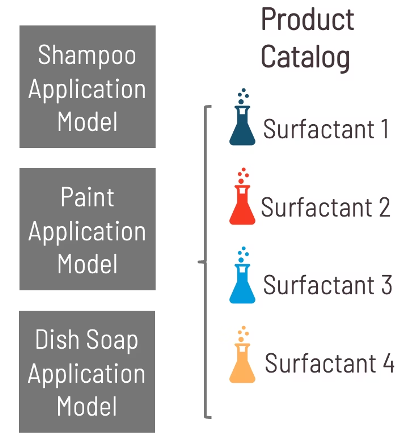
Multiple application models can be connected to the product catalog. Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
The Customer Challenge: Balancing Sustainability with Performance
Real-World Scenario
Consider a common request surfactant providers receive today: a major shampoo brand seeks to reformulate a popular product with plant-based surfactants to meet rising customer demand for natural ingredients. However, the reformulation must adhere to important performance standards that consumers demand.
Non-negotiable requirements include the following:
- Maintaining viscosity within established specifications
- Preserving the product's rheology profile
- Ensuring long-term formulation stability
- Matching or exceeding current performance benchmarks
The problem for the surfactant supplier is clear: which plant-based surfactant will work best in this particular formulation matrix, and at what concentration? Traditional procedures would require considerable experimental design, several testing cycles, and weeks or months to generate reliable suggestions.
The Stakes: Delays in responding to reformulation requests can lead to lost commercial possibilities, whilst hasty recommendations without proper testing risk product failures and strained customer relations.
Step 1 - Create The Application Model
Create a model to anticipate the attributes mentioned in the client request, such as viscosity, rheology type, stability, and cleaning power, based on your historical data and understanding of your customer's formulation and expectations. Run experiments to increase the model's accuracy and validate its predictions.
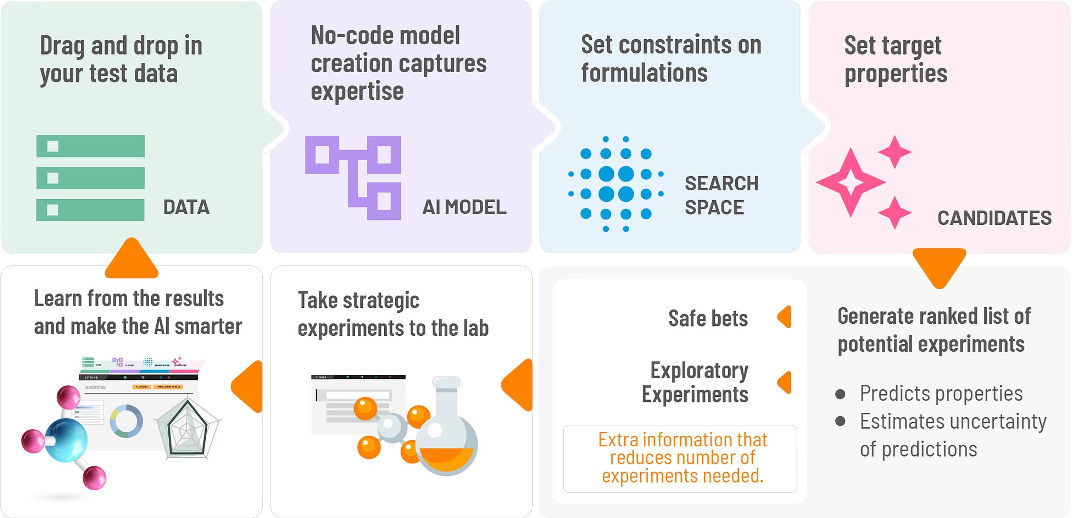
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
- Data Integration: Integrate historical experimental data, such as ingredient composition, processing parameters, and measured attributes. Ensure that the ingredients in your product catalog are well-defined.
- Molecular Characterization: Converting chemical structures to SMILES strings enables the computation of over 127 molecular descriptors.
- Model Training: Model training uses AI algorithms to find patterns between ingredient qualities, molecular traits, and performance results.
- Model Refinement: Small batches of experiments may be necessary to refine a model in response to a customer request that exceeds present capabilities.
Step 2 - From Data to Insights
Comprehensive Property Tracking
The platform records the following information for each constituent in the model dataset:
- Molecular structure encoded as SMILES strings for computational analysis
- Physical properties, including molecular weight, density, and solubility parameters
- Chemical characteristics, such as functional groups and reactive sites
- Performance attributes relevant to specific application areas
Simultaneously, measured attributes of final formulations are routinely documented, resulting in a rich dataset that connects molecular inputs and performance outputs.
This bidirectional data capture, from molecular characteristics to formulation composition to final properties, allows the AI to detect minor structure-property correlations that humans would miss.
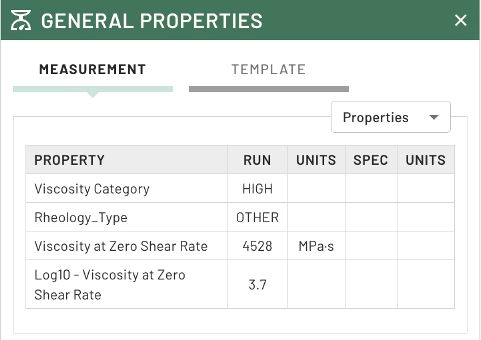
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
Shampoo Final Properties Stored
By modeling molecular structures as SMILES (Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System) strings, the platform generates over 127 molecular descriptors that capture critical structural aspects, functional group characteristics, and physical attributes.
Ingredient Properties Stored
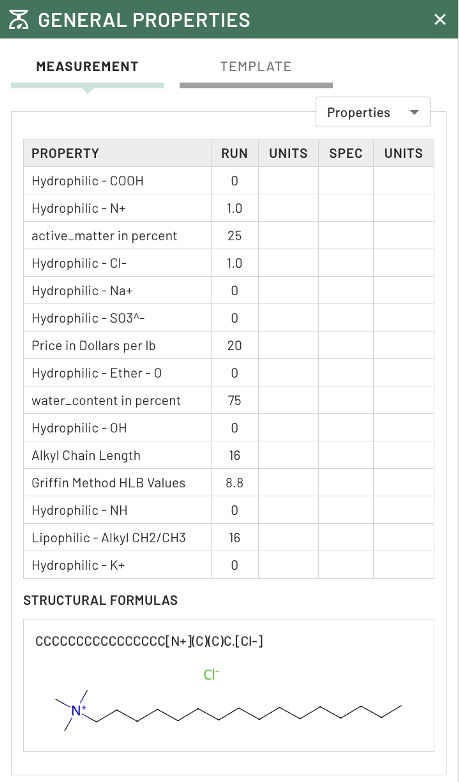
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
The predictive potential of AI-driven formulation platforms arises from their ability to link molecular structure to macroscopic performance, a relationship previously hidden in the tacit knowledge of expert formulators.
Data Visualization and Pattern Recognition
One of the most obvious advantages of platform-based formulation development is the capacity to see complex correlations in experimental data.
Traditional spreadsheet methodologies struggle to highlight multidimensional patterns, but AI platforms offer informative visuals that improve learning and hypothesis formulation.
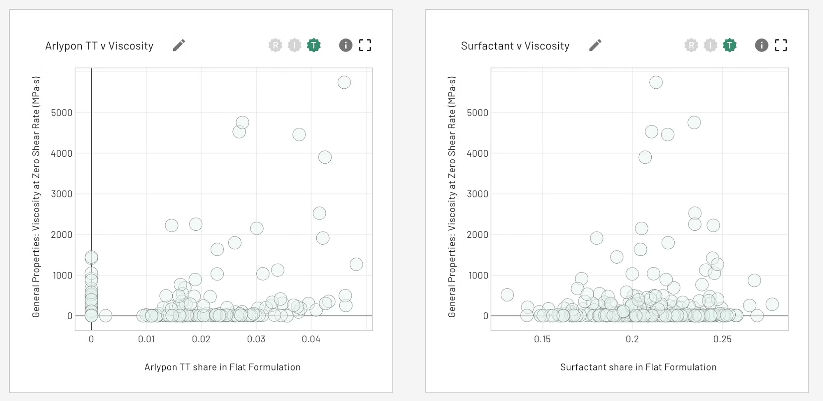
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
Consider the relationship between surfactant concentration and viscosity in the shampoo formulation example.
The platform display instantly exposes a non-linear relationship: viscosity climbs steadily as the surfactant share reaches around 22 %, then drops suddenly at higher concentrations. This discovery, which would otherwise need significant human plotting and analysis, becomes readily visible through automated data exploration.
- Trend Identification: Automatically find non-linear correlations and optimal operating windows across various variables to identify trends.
- Correlation Analysis: Identify unanticipated correlations between molecular traits, process parameters, and performance outcomes.
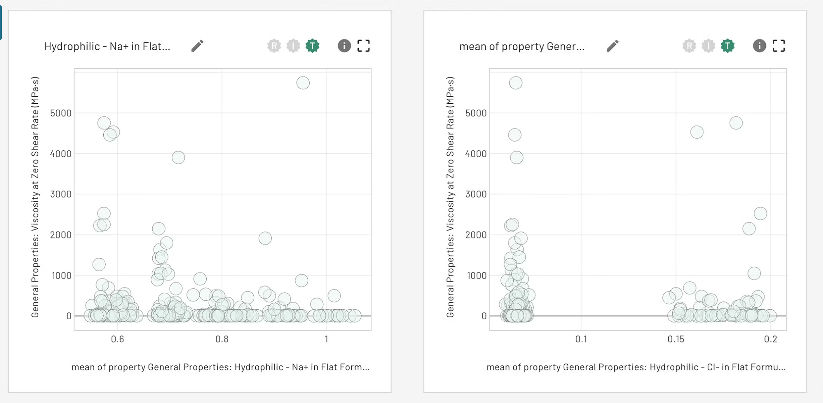
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
These visualizations serve several functions, including accelerating initial understanding of formulation behavior, supporting quality control by identifying anomalous results, facilitating communication between R&D teams and business stakeholders, and ultimately increasing confidence in AI models by demonstrating their foundation in real experimental data.
Step 3 - Check The Model and Learn from It
Feature Importance Analysis
The perceived "black box" aspect of machine learning algorithms is a major worry when using AI to make technical decisions.
Advanced platforms address this concern head-on with thorough interpretability features, particularly feature importance analysis, which identifies which elements have the most influence on expected outcomes.
When forecasting formulation stability, for example, the platform rates the relative relevance of several inputs such as constituent molecular descriptors, concentration ranges, process factors, and interaction effects. This transparency fulfills several critical functions for R&D leadership:
- Validation: Expert formulators can validate the AI's weighting of elements to ensure consistency with chemical principles.
- Discovery: Analysis might uncover unexpected elements that impact performance, providing fresh insights.
- Confidence: Understanding model thinking fosters confidence and trust.
- Improvement: Improve model predictions by collecting targeted data based on feature relevance.
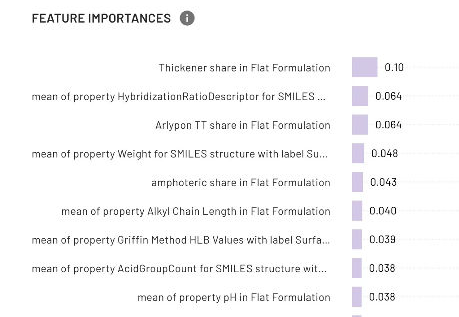
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
The metaphor of a "flashlight in a dark room" aptly conveys the value proposition: AI does not replace human expertise; rather, it enhances it by highlighting patterns and linkages that would otherwise be concealed in complex, multidimensional data fields.
This enhancement of human capability, rather than replacement, is the actual potential of AI in formulation creation.
Step 4 - Strategic Search Spaces
Search spaces are structured sets of constraints that limit the range of possible formulations to those that are technically feasible, financially viable, and regulatory compliant.
- Ingredient Constraints: Specify ingredient constraints, including substitutes (plant-based surfactants) and exclusions (parabens, sulfates). Multiple search spaces can handle regional regulatory differences.
- Concentration Bounds: Establish minimum and maximum concentrations for particular ingredients and ingredient classes to ensure proper formulation.
- Process Parameters: Determine acceptable ranges for mixing conditions, temperature profiles, pH adjustment processes, and other manufacturing variables.
Practical Example: Shampoo Reformulation
The search space for the plant-based shampoo project comprises the following:
- The supplier offers all plant-based surfactant options in their portfolio.
- Simple composition with no more than 10 ingredients.
- Product does not contain parabens or sulfates, meeting clean label regulations.
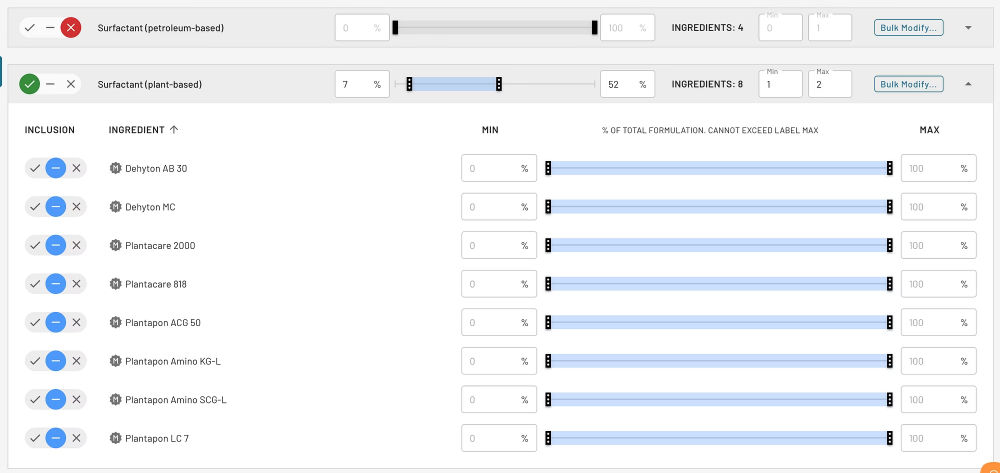
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
Step 5 - Set Targets and Run Model
After receiving a customer request, the technical services staff can use the Citrine Platform to:
A: Model Explore - Quick Property Predictions
Use Model Explore to forecast the attributes of novel formulations. For example, with plant-based surfactants replacing prior petroleum-based ones, the model can be used to determine whether the proposed formulation is predicted to be stable and have adequate viscosity.
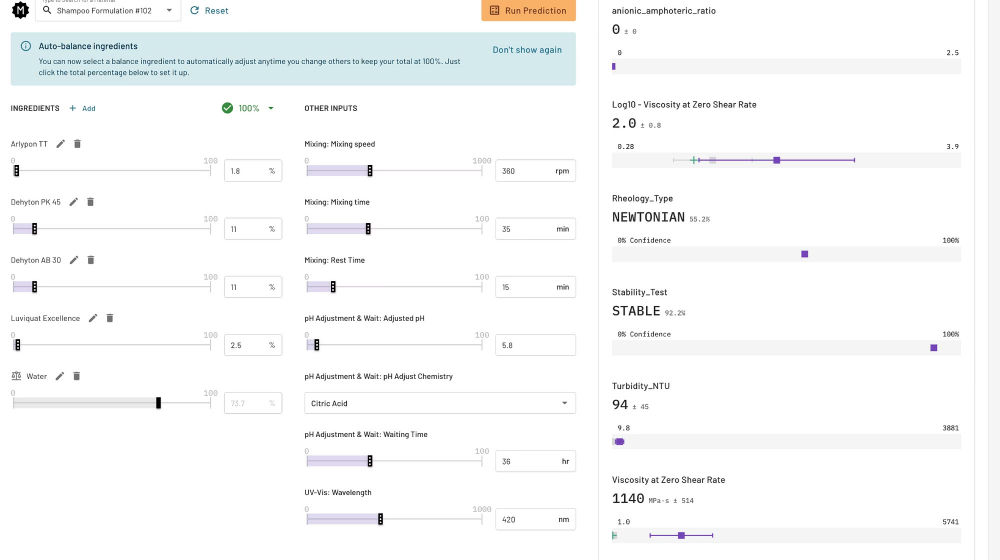
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
B: AI-Guided Experimentation for New Frontiers
If a request pushes the limits of present capabilities, resulting in high uncertainty in model predictions within a specific region of the search space (due to limited prior experimental data), the platform can handle it.
In such circumstances, the customer's desired qualities are assigned as targets, and the AI model is applied to the relevant search area to provide suggested tests.
These experiments are intended to either satisfy targets, demonstrate potential for future development, or improve the model's predictive power in the area required by the customer.
Once these experiments are completed and the model has been retrained and refined, it will be able to make exact recommendations on optimal surfactant performance, suggested quantities, and the technical performance that can be achieved with the surfactant.
Proven Results: Industry Case Study Demonstrates Transformative Impact
The theoretical benefits of AI-driven formulation development are translated into practical business outcomes in the chemicals and consumer products industries. A typical case study demonstrates the platform's adaptability.
Stepan Company: Scaling AI Across Multiple Projects
Stepan® is a global specialty and intermediate chemical provider of chemical ingredients and formulations. They first tested AI-driven formulation creation for a liquid dishwashing project.
The business manager's positive response – "I’d love to have 10 of these projects going" – reflects the platform's capacity to drive deeper technical talks with clients while also boosting internal efficiency.
The reusable model structure enables Stepan to respond quickly to various client reformulation requests, turning technical assistance from a cost center into a competitive differentiator.
- Liquid Dishwash Formulations: Reuse models, datasets, and search spaces for future projects.
- Crop Protection Formulations: For crop protection formulations, predict surfactant stability and appearance for customer uses.
- Spray Foam Formulations: Improved Polyol compositions for Spray Foam Insulation.
I’d love to have 10 of these projects going. I want more application data to drive deeper conversations around subjects our customers care about.
Stepan Business Manager for the Liquid Dishwash Project
The Path Forward: Accelerating Your Materials Innovation Journey
Strategic Imperatives For R&D Leadership
For R&D directors and technical service leaders analyzing this possibility, several strategic factors deserve attention:
- Platform thinking: Think of AI adoption as a platform, rather than a one-time effort.
- Data readiness: Organize historical experimental data to maximize near-term ROI.
- Cultural preparation: Encourage openness to AI-powered workflows and decision-making.
- Pilot selection: Identify high-value client relationships where improved responsiveness leads to a competitive advantage.
- Expertise partnership: Partner with vendors with proven implementation experience to accelerate adoption.
- Respond quicker: Improve technical support by shifting from reactive problem-solving to proactive solution delivery, leading to increased customer satisfaction and corporate success.
- Adopt easily: The platform architecture interfaces with existing laboratory operations and data systems, reducing disturbance during adoption.
- Trust experience: Collaborate with experienced teams who have successfully used AI in chemicals and materials organizations over the past decade.

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Citrine Informatics.
For more information on this source, please visit Citrine Informatics.