It has been demonstrated in the past that using Borate fusion with the M4TM gas fluxer together with Wavelength Dispersive XRF (WD- XRF) has the preferred qualities to conform to the analytical targets specified in the ISO/DIS 29581 -2 and the ASTM C-114 international standard methods.
With increasing demand for electric fusion instruments in the cement industry, it is important to assess the performance of LeNeo® electric fusion device to evaluate its capacity. This way, compliance to the analytical standard test methods (ISO and ASTM) using the same calibration approach as with the M4TM Fusion instrument can be ensured.
In this article, the performance assessment of LeNeo® instrument and its conformity to the two standard methods is made by recreating the same analytical method employed for assessing the M4TM gas fluxer. The article also highlights the results of a novel calibration approach that facilitates the analysis of chlorine (Cl) in cement materials through a borate fusion and WD-XRF method.
Experimental Method
Apparatus and Instrumental Conditions
A Claisse® LeNeo® automatic electric fusion instrument was utilized to produce all the fusion disks. The instrument has pre- set fusion programs, excellent insulation properties, and a resistance-base electric heating system, which enabled homogeneous heating conditions and provided reproducible and repeatable fusion conditions with excellent retention of the volatile elements.
For preparation of ignited samples and for LOI determinations, a Fisher Scientific Isotemp®programmable muffle furnace was utilized. The LOI technique, which was utilized for all cement clinkers, included ignition at 950°C temperature in a platinum crucible for 1h. Data was collected using the Bruker-AXS S4 Explorer sequential WDXRF spectrometer.
Table 1. Chlorine Kα calibration analytical line parameters
| |
|
| kV: |
40 |
| mA: |
25 |
| Vaccum: |
Yes |
| Filter: |
None |
| Crystal: |
Ge |
| Collimator: |
0.46° |
| Detector: |
FPC |
| Mask: |
28 mm |
| Peak Position: |
92.782 °2? |
| Counting Time: |
30 s |
| Background: |
93.603 °2θ |
| Background Time: |
30 s |
Global Sample Preparation Method
The sample preparation method employed prior to the fusion was similar to the one employed for the M4TM Claisse gas fluxer. For the experiment, 0.6000g ± 0.0001g of ignited sample was weighed in a clean 95% platinum/5%gold crucible, and 6.0000g ± 0.0003g of Claisse LiT/LiM/ LiBr: 49.75%/49.75%/0.5%, Pure Grade Flux was added to the sample.
The flux and sample were then combined in a VortexMixer™. The LeNeo® fusion temperature was maintained at 1065⁰C for a period of 19 minutes, and the molten material was poured into a 95% platinum/5%gold mold. The automatic cooling process of the glass disk was achieved in 5 minutes with forced air.
Calibration Strategy, Selection of Control Sample and Preparation for Validation
Two individual sets of CRMs, one from the JCA and the other from the NIST, were utilized for the calibration of cement application. This procedure is similar to the assessment of the M4TM Claisse gas fluxer.
Table 2 displays the CRMs element concentration as an oxide equivalent for the two sets of LOI free base. It also shows the element concentration of the control sample chosen to assess the global borate fusion and XRF method with ISO international standard method.
Table 2. CRMs element concentration as an oxide equivalent and control sample
| Compound |
Concentration Range |
ISO Control sample |
| NIST – JCA (LOI Free Base) |
BCS-RM 354 (LOI Free Base) |
| SiO2 (%) |
18.907 - 29.29 |
21.8 |
| Al2O3 (%) |
3.40 - 10.70 |
4.85 |
| Fe2O3 (%) |
0.154 - 4.18 |
0.30 |
| CaO (%) |
49.28 - 68.94 |
70.00 |
| MgO (%) |
0.78 - 5.12 |
0.42 |
| SO3 (%) |
1.91 - 4.689 |
2.25 |
| Na2O (%) |
0.021 - 1.086 |
0.10 |
| K2O (%) |
0.094 - 1.248 |
0.11 |
| Cl (%) |
0.0019 - 0.0183 |
0.005 |
Given that only a few cement CRMs include a high chlorine level, the calibration for Chlorine needs to be carried out with synthetic standards. Known concentrations of Chlorine salts were added to existing cement CRMs to produce a calibration range from 0% to 0.567%.
Results and Discussion
Robustness of the Fusion Methodology
The LeNeo® fusion instrument is capable of fusing samples of raw materials, cement, and cement-related materials into glass disks, within the same range as the M4TM gas fluxer. Sample ignition before fusion is necessary to achieve success with all the raw materials.
Chlorine Calibration
The calibration curve of the corrected concentrations against the predicted concentrations is shown in Figure 2. This calibration curve ensued from the calibration approach based on the usage of commercial cement CRMs with added chlorine salts (Figure 1). The curve’s linearity shows a excellent retention of the Chlorine in the cement glass disks.
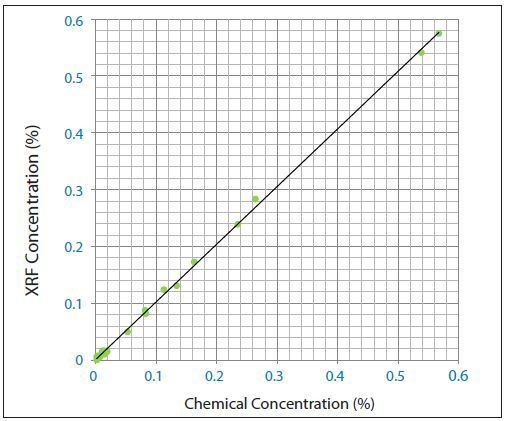
Figure 1. Chlorine (Cl) calibration curve made from cement CRMs with added chlorine salts.
ASTM Precision and Accuracy
The ASTM accuracy and precision tests were then applied. Table 3 shows the accuracy result, which displays the maximum values of variation between the certified value and average duplicate results across all the analyzed CRMs. The precision results show the largest absolute variation of the duplicates across all the CRMs utilized for all inspected elements.
Table 3. ASTM C 114: Results of the precision and accuracy tests
| Compound |
Precision Test |
Accuracy Test |
| ASTM Limit |
LeNeo Fluxer |
ASTM Limit |
LeNeo Fluxer |
| SiO2 (%) |
0.16 |
0.087 |
± 0.2 |
0.104 |
| Al2O3 (%) |
0.20 |
0.060 |
± 0.2 |
0.078 |
| Fe2O3 (%) |
0.10 |
0.019 |
± 0.10 |
0.022 |
| CaO (%) |
0.20 |
0.142 |
± 0.3 |
0.150 |
| MgO (%) |
0.16 |
0.029 |
± 0.2 |
0.063 |
| SO3 (%) |
0.10 |
0.028 |
± 0.1 |
0.061 |
| Na2O (%) |
0.03 |
0.012 |
± 0.05 |
0.018 |
| K2O (%) |
0.03 |
0.011 |
± 0.05 |
0.026 |
| Cl (%) |
0.003 |
0.003 |
N/A |
0.004 |
ISO Precision and Accuracy
The ISO accuracy and precision tests were then applied. Table 4 shows accuracy results, which are the maximum difference between the certified value and a single replicate, while the precision results are the largest absolute variation of the successive results of the BCS-CRM 354 control sample for all the inspected elements.BCS-CRM 354 control sample for all the inspected elements.
Table 4. ISO/DIS 29581-2: Results of the precision and accuracy tests
| Compound |
Precision Test (BCS-RM 354) |
Accuracy Test (BCS-RM 354) |
| ISO Expert Limit |
LeNeo Fluxer |
ISO Expert Limit |
LeNeo Fluxer |
| SiO2 (%) |
0.134 |
0.044 |
0.15 |
0.089 |
| Al2O3 (%) |
0.062 |
0.028 |
0.08 |
0.067 |
| Fe2O3 (%) |
0.023 |
0.005 |
0.02 |
0.018 |
| CaO (%) |
0.244 |
0.121 |
0.25 |
0.159 |
| MgO (%) |
0.023 |
0.009 |
0.02 |
0.020 |
| SO3 (%) |
0.054 |
0.019 |
0.08 |
0.027 |
| Na2O (%) |
0.023 |
0.010 |
0.02 |
0.019 |
| K2O (%) |
0.023 |
0.003 |
0.02 |
0.003 |
| Cl (%) |
0.023 |
0.003 |
0.02 |
0.002 |
Conclusion
LeNeo® electric fusion instrument exhibits the same analytical performance and fusion capabilities as the M4™ Claisse fluxer®, which is used as a reference in the cement industry. LeNeo® electric fusion instrument not only allowed to qualify for the ASTM C-114 standard test method, but also conformed to the ISO/DIS 29581-2 standard test methods for all relevant elements in the cement industry.
In addition, the excellent control of the fusion conditions allowed perfect retention of all the volatile elements as well as chlorine for which an innovative calibration approach facilitated its precise analysis.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Claisse.
For more information on this source, please visit Claisse.