
Application
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a multipurpose thermoplastic, is used for construction, floor coverings, packaging, bottles, coatings and tubing. PVC can be hard or flexible, based on the quantity of fillers, plasticizers, additives and pigments added. Every individual type of PVC is obtained by mixing the PVC resin and fixed quantities of chosen additives.
It is significant that the plasticizer content is within specification limits to make sure that the product has the desired hardness and flexibility for use. The MQC+ benchtop analyzer can find out plasticizer content quickly and accurately without using environmentally hazardous solvents or complex chemometrics.
Advantages of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
The conventional method of testing involves dissolving the plasticizer in organic solvent and finding out the quantity of dissolved oil in the solvent by gravimetric analysis (following distillation), infrared spectroscopy or gas chromatography. These methods require expert operators, consume more time and use dangerous solvents. Another way to indirectly determine the plasticizer content is by Near Infrared (linked with chemometric analysis) or by mechanical testing of the product flexibility or hardness.
A rapid, easy to operate, easy to calibrate, alternative method is provided by the MQC+ benchtop Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) analyzer. This method requires less sample preparation. Actually, it is best suited for routine operation in a production or laboratory environment without any necessity for extra chemicals or specialist operator training.
Method
Benchtop NMR can differentiate between signals from solid (dense, ordered crystallites) and amorphous regions within samples. This is because solid signals weaken rapidly (in the order of a few tens of microseconds), but the amorphous signals last longer (many hundreds of microseconds).
As the NMR signal from the amorphous parts increases, it can be directly correlated to, the percentage plasticizer content. In some cases, it is necessary to increase the temperature to enhance the plasticizer mobility and hence the signal-to-noise of the measurement. Moreover, as the mobility of the plasticizer phase is highly sensitive to temperature, it is necessary to make the temperature of the polymer stable before measurement, which is generally at 40 °C, the same as the magnet.
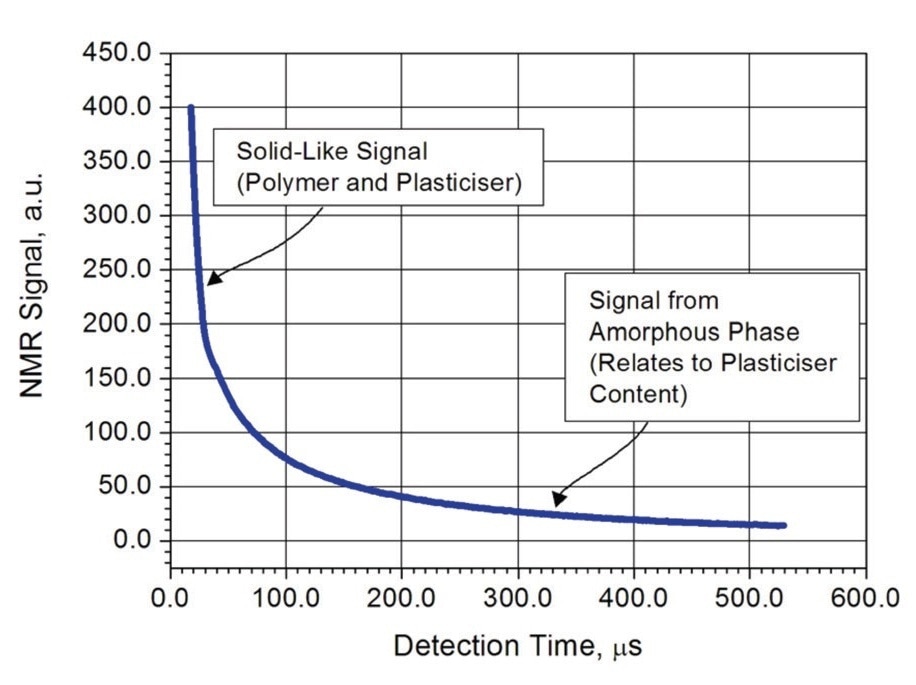
Figure 1. Typical NMR signal from polymer.
Calibration
Only two well-known standards are needed to calibrate the MQC. However, it is recommended that the instrument is calibrated using 3-6, or preferably more, standards with known plasticizer contents uniformly spread over the range of interest. NMR cannot be more accurate than the reference technique to which it is compared, as it is a comparative technique. By inspecting more reference samples, error is minimized.
Measurement
26 mm glass NMR tubes are filled with PVC samples up to a stipulated level and weighed. Prior to analysis, the sample tubes are placed in a temperature controlled conditioning block at 40 ºC for at least 20 minutes for optimal precision. Measurement time for each sample is 16 seconds.
Results
Figure 1 indicates that a plain linear calibration can be produced using just four PVC samples with plasticizer content values ranging from 18 to 40% yielding a standard deviation of 0.16%. Every plasticizer used will require a different calibration. By taking 10 consecutive repeats of the same sample at 35%, the precision of measurement is found to be +/- 0.06%.
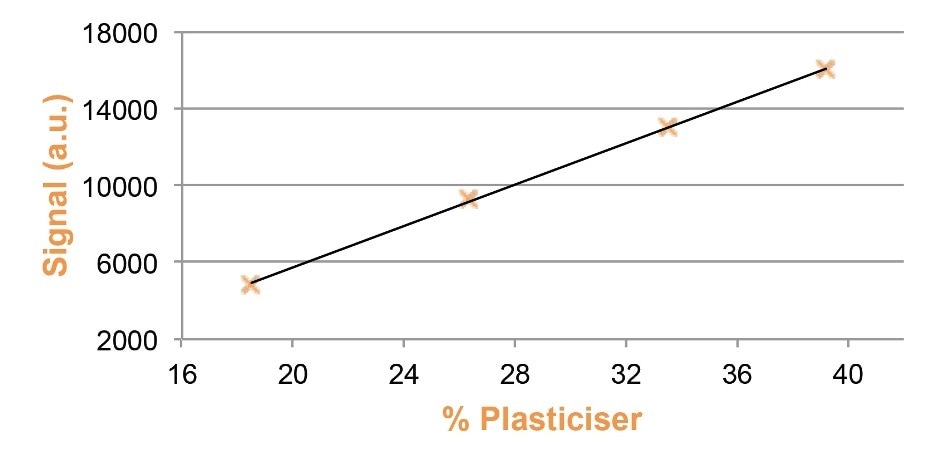
Figure 2. NMR calibration for plasticizer in PVC.
Conclusion
- NMR is very stable over the long term and rarely needs calibration adjustment
- NMR is insensitive to the air voids between the pellets or grains of powder
- Excellent measurement precision compared to wet chemistry methods
- Quick sample measurement time
- The same sample can be measured many times before being tested by other techniques, as the NMR technique is non- destructive
Complete Package
Oxford Instruments provides a package that is especially customized to the measurement of plasticizer content in PVC.
- MQC23+ Benchtop NMR Analyzer including:
- 0.55 Tesla (23 MHz) high homogeneity magnet
- Probe for 26 mm diameter sample tubes (14 ml sample volume)
- Integrated system controller (no external PC required)
- Integrated flat-screen display
- MultiQuant software including RI Calibration, RI Analysis and the EasyCal ‘Plasticizer in PVC’ application
- Test/tuning samples
- 26 mm glass tubes
- PTFE stoppers
- Stopper insertion/removal tool
- User manuals
- Method sheet
Optional Items
- A dry heater and aluminum block with holes for sample conditioning at 40 °C
- A precision balance

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Oxford Instruments Magnetic Resonance.
For more information on this source, please visit Oxford Instruments Magnetic Resonance.