The majority of people have a GPS device with them at all times. What used to be limited to military and commercial applications has now expanded to include automobiles and committed consumer GPS devices.
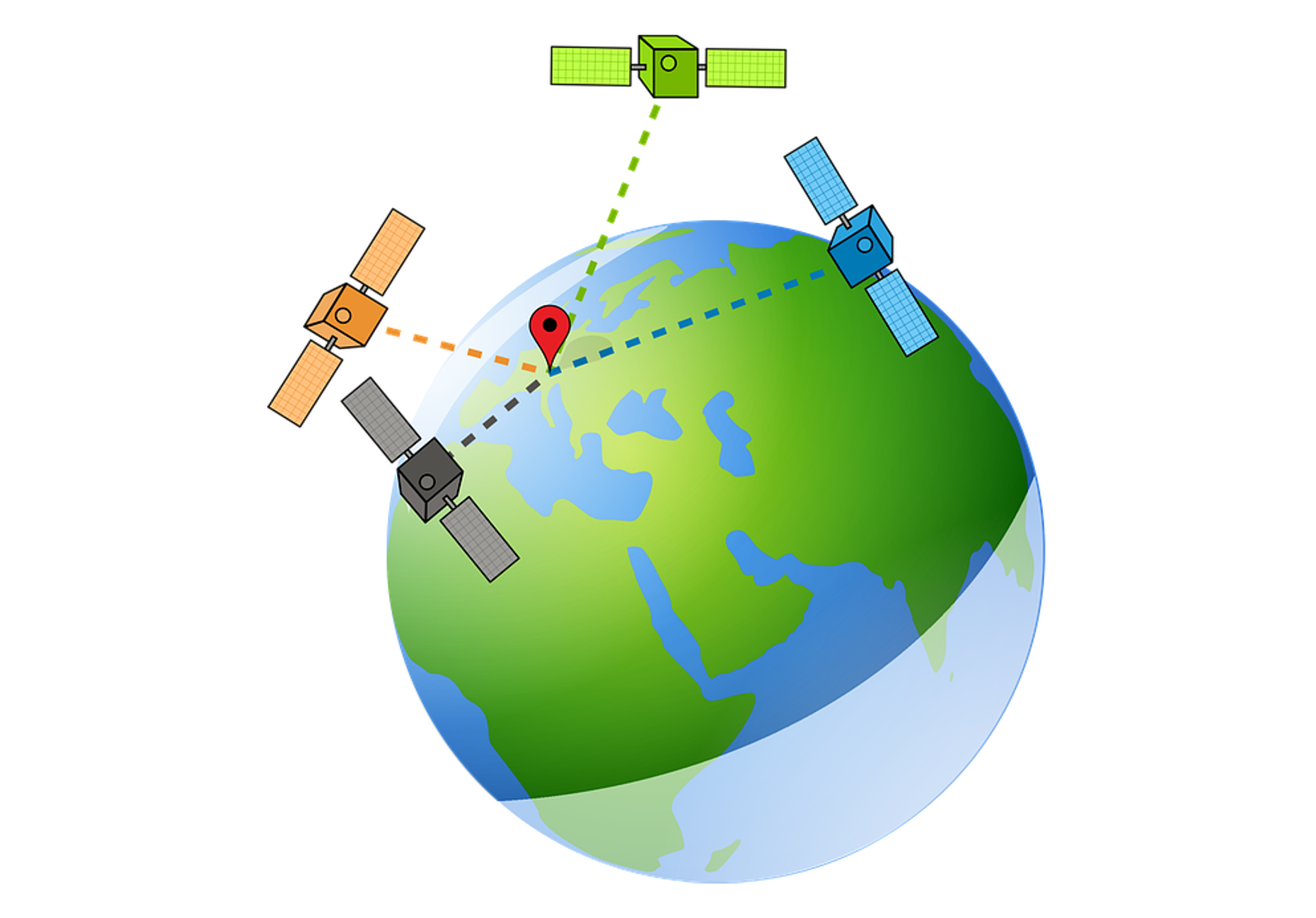
Image credit: Superior Sensor Technology
Many portable electronic devices, like smartphones and tablets, now include a built-in GPS receiver with a variety of mapping apps that can be used to detect the location or provide directions to another location.
How GPS Works
GPS receivers communicate with satellites to compute three values:
- Latitude of the GPS receiver: Latitude refers to the device’s location north or south of the equator.
- Longitude of the GPS receiver: Longitude refers to the device’s location distance east or west from an imaginary line linking the North and South Poles, known as the Prime Meridian.
- Elevation of the GPS receiver: Elevation refers to the device’s height above (or below) sea level.
These three characteristics combine to form a three-dimensional geographic coordinate system that pinpoints a location on earth. The elevation is usually measured in meters, while latitude and longitude are calculated in decimal degrees.
These coordinates are used as an input value by mapping software to plot the device’s location on a map. The three-dimensional coordinates are updated regularly as the device moves, and the software updates the plot on the map.
Pressure Sensors Improve 3-Dimensional GPS Accuracy
Structures can interfere with GPS signals. Buildings, tunnels, and other objects in urban areas can obstruct and impair the signal received by the GPS receiver from satellites. All three coordinates, latitude, longitude, and elevation, can be affected.
Out of the three coordinates, pressure sensors can assist a GPS application to ascertain the device’s elevation more precisely. A barometric pressure sensor, in particular, can be used to supplement the GPS signal in identifying the device’s elevation above sea level.
There are numerous occasions when knowing a position’s exact altitude is critical. For instance, GPS is useful in a variety of indoor applications. While searching for someone or something in a shopping mall, an office building, a stadium, a multi-story parking structure, or an airport, knowing which level to go to makes it a lot easier.
Tracking valuable assets is another indoor GPS application. Asset tracking, or knowing where an item is at all times, is critical in a variety of commercial and industrial applications. It is hard to ascertain where something is in a large, multi-storey complex if the precise floor is not known.
A barometric pressure sensor, which is built into several electronic devices, including most newer smartphones, allows for precise indoor navigation. Since the iPhone 6, Apple has included barometric sensors. Barometric pressure sensors are found in a number of popular Android smartphones, including those from Samsung, OnePlus, and others.
NimbleSenseTM Architecture Improves GPS Elevation Measurement
The NimbleSense architecture, with its extremely low noise floor, is best suited for the accurate indoor elevation measurements that GPS solutions need to maximize their performance and accuracy. Superior’s barometric and absolute pressure sensors are less affected by external interference and noise, resulting in more precise measurements that are typically within ±1 m, greatly reducing potential calculation errors.
The benefits of NimbleSense go far beyond the low noise floor, as the architecture’s advanced digital filtering offers significant advantages. External sounds, vibrations, and rapid movements can all influence the accuracy of pressure sensors in smartphones and other devices with embedded GPS.
Superior’s pressure sensors use integrated advanced digital filtering technology to remove noise generated by these factors before it impacts product performance. As a result, the noise is reduced before it becomes an error signal, thus greatly reducing erroneous readings.
Conclusion
GPS receivers are with us at almost all times. They are being used more frequently indoors, in addition to mapping X, Y coordinates. Barometric pressure sensors are used to ascertain the device’s altitude (the Z coordinate) to accurately measure indoor locations (thus expanding from X, Y to X, Y, Z).
Absolute and barometric pressure sensors are a simple and cost-effective solution. Due to the NimbleSense architecture, which has the industry’s lowest noise floor and advanced digital filtering, Superior Sensor Technology’s pressure sensors provide the greatest possible levels of accuracy.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Superior Sensor Technology.
For more information on this source, please visit Superior Sensor Technology.