The bipolar FUSION PTR-TOF technology enables rapid switching between multiple reagent ions, significantly broadening the application range without compromising the flexibility of this all-in-one analyzer generation.
No hardware or reactor changes are needed. With push-button simplicity, the bipolar FUSION PTR-TOF sets a new benchmark in trace gas analysis for demanding applications.
Advantages of Multiple Reagent Ions to Characterize Oxidation and Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation
Proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry (PTR-MS) is a widely used method for characterizing Secondary Organic Aerosols (SOAs) and their precursors.
Advanced instruments such as the recently introduced FUSION PTR-TOF not only use the proven H3O+ reagent ions for quantitative measurements across a wide range of organic compounds, but also offer additional ionization modes such as NH4+ for soft adduct ionization, enabling the detection of highly oxidized compounds.
Complemented by the NO+ and O2+ ionization modes, this instrument supports the detection of the vast majority of both organic and inorganic compounds.
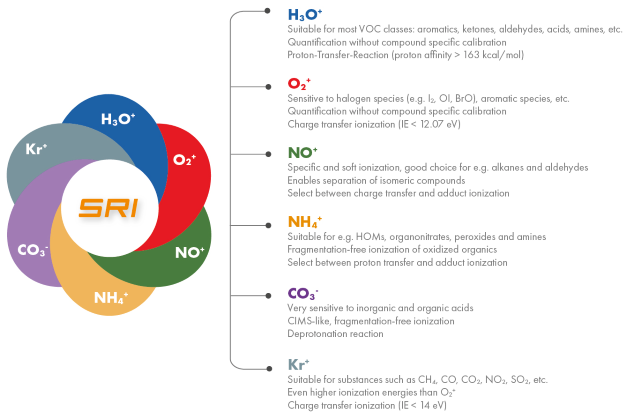
Image Credit: IONICON Analytik
Fast Reagent Ion Switching
A key advantage of the system is its ability to rapidly switch between positive ionization modes in seconds, made possible by the Invion Source. This allows efficient analysis of different compound classes in a short time.
As shown in Figure 1, the instrument can quickly and reproducibly switch between ionization modes (O2+, H3O+, and NH4+) and between E/N settings for H3O+. This flexibility improves both sensitivity and selectivity by tailoring ionization conditions for specific compound types.
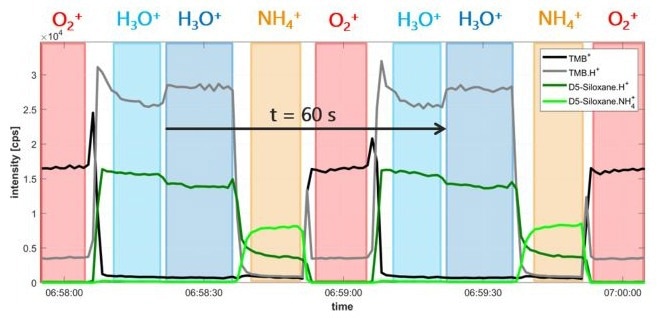
Figure 1. Demonstration of the instrument’s capability for fast and reproducible switching between ionization modes (O2+, H3O+, NH4+) and E/N for H3O+, supporting time-resolved multi-mode analysis. Image Credit: IONICON Analytik
Selective Ionization of Acids with CO3-
The next-generation FUSION PTR-TOF mass spectrometer includes electronics for negative mode CO3- ionization and fully automated switching between positive and negative modes.
Using CO3- ionization, the system detects organic acids such as perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids, and inorganic acids like SO2, H2SO4, and HNO3 with great selectivity and sensitivity.
Products like limononic acid, for example, are identified with great efficiency and little fragmentation because they facilitate a soft ionization process with low fragmentation.
Figure 2, which compares the resultant ions of several acids following H3O+ and CO3- ionization, also makes the latter quite evident. Figure 3 demonstrates the ability to switch between modes at the press of a button, without hardware changes.
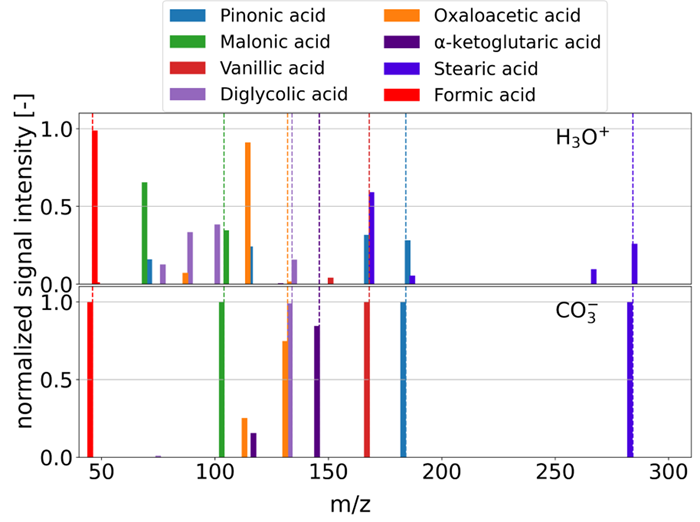
Figure 2. Comparison of H3O? and CO3? ionization modes, highlighting the enhanced capability of CO3? ionization for the selective detection of acids with reduced fragmentation. Image Credit: IONICON Analytik
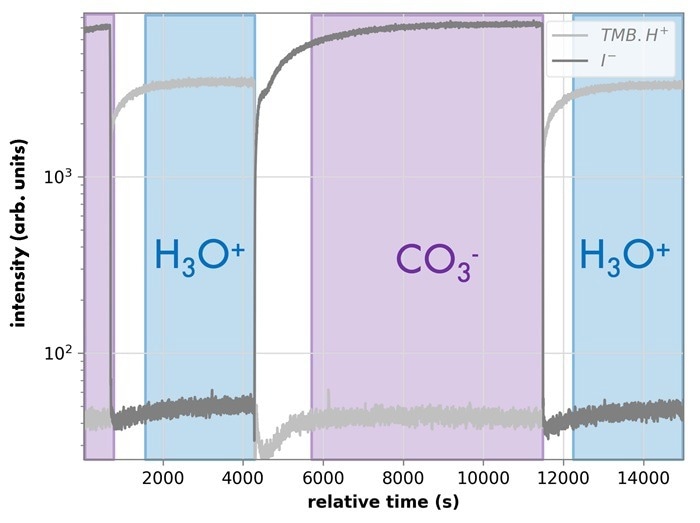
Figure 3. Bipolar switching between CO3? and H3O? ionization modes. Image Credit: IONICON Analytik
Conclusion
- CO3- is highly selective toward the formed acids
- Compounds like limononic acid are detected effectively with minimal fragmentation
- Sequential use of H3O+, NH4+, NO+, and CO3- modes enables comprehensive analysis of SOA formation

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by IONICON Analytik.
For more information on this source, please visit IONICON Analytik.