As regulatory limits phase out certain raw materials, the chemical industry is increasingly turning to AI to accelerate the search for viable alternatives.
The Citrine Platform uses chemical formulas and molecular structures to automatically compute important "features".
This is accomplished by encoding molecular structures into computer-readable formats such as SMILES (Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System). Encoding structures like this enables the computation of a variety of molecular parameters, such as the number of hydrogen bonds, polarizability, and molecular weight.

Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
AI-Powered Analysis
As AI models examine these features to identify their importance in obtaining target properties, they efficiently evaluate alternative compounds that share these critical characteristics.
AI-Powered Analysis
By helping scientists to find feasible substitutes, AI helps companies reformulate products more quickly and effectively, expediting compliance with changing laws.
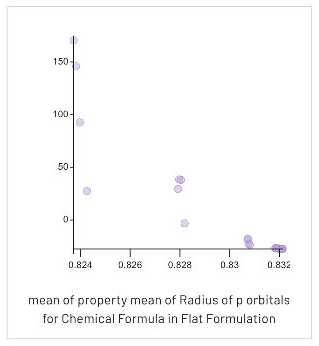
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
Patented Technology
Using Machine Learning to Explore Formulation Recipes with New Ingredients
Patent granted No. 10,984,145 B1
This technique ranks candidate formulation recipes according to their chances of meeting desired criteria. These recipes may include previously untested ingredients.
Case Study: Removing PFAS in Adhesives
- Two years saved on R&D work on a five-year project timeline
- 30 viable candidates narrowed from millions of formulations
The Challenge
A global materials corporation was under increasing pressure to reformulate its pressure-sensitive adhesives product line to eliminate PFAS chemicals.
The challenge involved expediting product development to meet rising regulatory demands for PFAS removal while preserving the existing mechanical performance and navigating a complex formulation space with various variables and constraints.
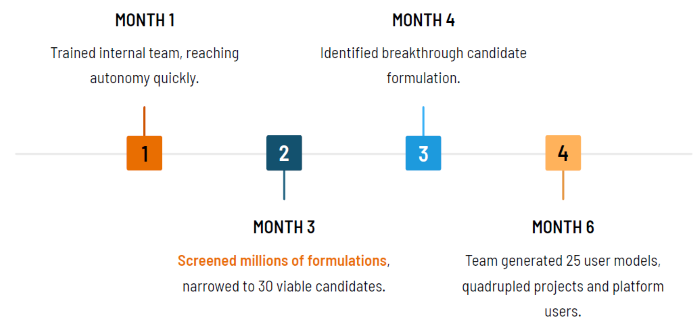
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
Case Study: Reformulating Plastics for Safety
Replacing Toxic Ingredients While Retaining Technical Performance
Award # ITE-2236190 | TIP C-Accel, PM Linda Molnar
Collaborating Partners and Funding Institution

The Challenge
Toxic compounds in PVC plastics are being increasingly studied and phased out, particularly phthalate plasticizers. However, the mechanical performance of PVC is unclear when non-toxic substitutes are used. The goal is to find PVC formulations that remove phthalates while retaining flexibility.

Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
The Process
- Collected data on plastic chemicals (plasticizers, fillers, stabilizers, lubricants) and PVC formulations.
- Developed machine learning models to forecast mechanical performance and toxicity.
- Optimized plastic formulations for both mechanical performance and toxicity restrictions.
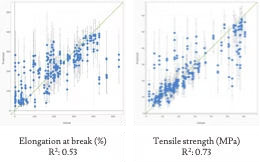
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
The Results
Quantitative comparison of technological (T) performance with and without environmental (E) and societal (S) restrictions. Engineers can now calculate the cost of meeting regulations or supply chain restrictions.
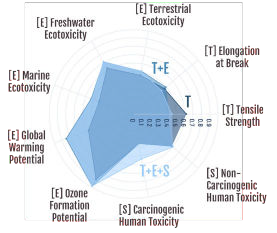
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Citrine Informatics.
For more information on this source, please visit Citrine Informatics.