Huntsman Building Solutions, a major manufacturer of spray foam insulation, is using its 110 years of knowledge to pioneer an energy-efficient, dependable, and sustainable polyurethane spray foam insulation for a variety of applications.
“In the old workflow, it took a chemist six months to come up with a starter formulation. With the [Citrine Informatics] platform, they can get a starter formulation on day one.”
Executive Summary
Huntsman Building Solutions used the Citrine Platform to:
- Reduced reliance on full-scale fire testing
- Shortened development time
- Delivered a high-performing, sprayable, and regulation-compliant foam
Objectives
Huntsman prioritizes meeting flammability laws, however, large-scale fire tests (such as ASTM E84) are complex, expensive, and time-consuming as they are performed off-site by an independent tester. They are an essential component of regulatory testing for product certification and a significant milestone in R&D. They are carried out once the formulation has been fine-tuned and the team is confident, based on small-scale fire tests conducted internally, as well as testing of other critical qualities.
Huntsman wanted to:
- Create a development approach that combines deep chemical expertise with rapid data-driven iterations
- Create a formulation that meets ASTM E-84 standards
- Reduce the requirement for large-scale fire tests
- Improve materials' understanding of complex chemistry
Goal: Make the initial formulation of AI002 compatible.

Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
The Process
Data
The earlier large-scale fire tests on AI002 and related formulations were insufficient to generate a relevant model. Therefore, this data was supplemented with data from small-scale fire testing.
These tests generate data over time, which is represented as a curve on a chart. The team used its knowledge to choose key features from these charts to convert into data for training the models.
It is also widely acknowledged that the Isocyanate index (the ratio of isocyanate (NCO) groups to total active hydrogen) is critical for polyurethane foam manufacturing.
The Citrine Platform automatically calculates ingredient ratios and generates molecular information about an ingredient via SMILES or InChI notation, which can then be used as a model input.
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
Search Space
The initial formulation AI002 included polyols, flame retardants, a surfactant, blowing agents, catalysts, and isocyanate.
The Huntsman team applied their expertise to create a search area in which various options for each type of chemical could be explored while maintaining a realistic expectation of acceptable fire performance, based on their previous experience.
There are so many formulas that can be created by combining these substances; testing them all would be impractical.
Modeling
Modeling included estimating ASTM E-84 smoke growth and flame spread, as well as R-value (thermal insulation). Other formulation features known to improve fire performance were estimated and used as input for models.
Iterative Experimentation
One of Huntsman's objectives for this project was to create and verify a new development framework, transitioning to an iterative AI-driven experimentation approach. It’s uncommon for a corporation to have enough data on the specific formulation type they are working on to create a flawless model in one go.
Repeated studies and use cases have demonstrated that adopting an AI-driven iterative experimentation technique can lead to target values faster than trial and error.
Sequential Learning is the process by which a batch of experiments is suggested based on their likelihood of success, the experts decide which to take to the lab, and the results of the experiments are uploaded back into the Citrine Platform to improve the AI model's accuracy and ability to recommend the next set of experiments.
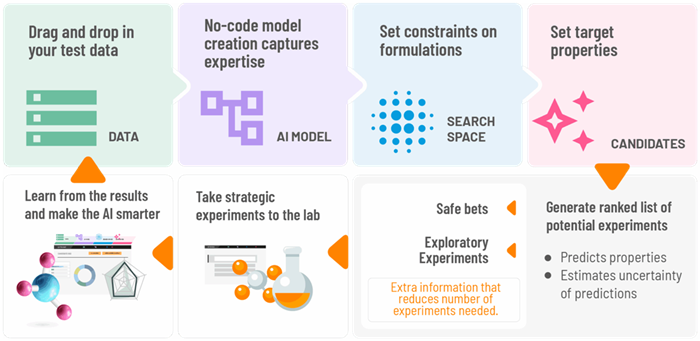
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
Once the initial predictive models were constructed and demonstrated promise, a sequential learning procedure was employed to get closer to the target values for smoke generation and flame spread.
Huntsman employed two methods to improve AI models in between rounds of research. They not only uploaded test results, but they also improved the functionality of the small-scale fire tests.
The Results
Better Understanding of the Domain
Nuanced behavior during small-scale studies was "featurized". Each feature might then be examined to determine its effect on flame spread, smoke formation, and insulating characteristics.
Compliant Formulation
R1.3-FR, a modified AI002 formulation, outperformed expectations in fire resistance, sprayability, and physical performance testing.
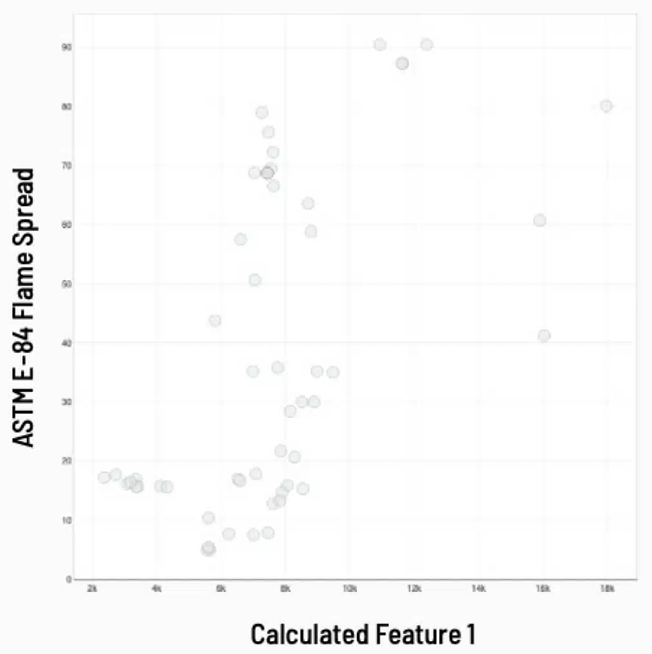
Image Credit: Citrine Informatics

Image Credit: Citrine Informatics
Increased Productivity
The iterative procedure, which was supported by data-driven prioritizing and experimental validation, decreased wasted effort while also unlocking new material understanding. The team can now prioritize, anticipate, and develop successful formulations quickly and accurately.
Summary and Next Steps
This breakthrough was not an isolated event, but rather a significant stride forward in Huntsman's development process. The team increased confidence in AI-generated insights, reduced dependency on full-scale testing, shortened development time, and produced a high-performing, sprayable, and regulation-compliant foam.
This project's accomplishment paves the way for future innovation not only in sprayable polyurethane foam but also in other rigid foam systems that require great fire performance while remaining efficient, compliant, and commercially viable.
This makes AI/ML partners in innovation, not just a recommender.
Rogerio Drummond De Souza, Technical Director of Specialties and Roofing Products

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Citrine Informatics.
For more information on this source, please visit Citrine Informatics.