Volumetric Karl Fischer (KF) titration is optimized for rapidly and accurately determining water content in a wide range of samples. It is based on the reaction of water with iodine, sulfur, an amine base, dioxide, and a short-chain alcohol, which also typically serves as the solvent for the reaction.
The KF technique can be used with solids, liquids, and gases as long as the water present in the sample matrix can be released and subsequently titrated by the KF reagent.
The release of water into the KF solvent is often straightforward in the case of liquids and gases. However, it becomes much more challenging for creams, pastes, and solids, particularly when these do not readily dissolve.
Dissolution can be supported through the addition of a cosolvent with a different polarity than alcohol or heating the KF cell, but this approach typically only works to a certain extent.
It is possible to extract the water from these samples into a suitable solvent externally; adding these directly to the cell and reducing them using a homogenizer is much quicker and more convenient.
Homogenizers are high-speed, high-shear stirrers that efficiently disperse powders and shred a wide range of solids, including pills, candies, dried fruits, and coffee beans. Using homogenizers avoids labor-intensive sample preparation, often significantly shortening analysis time.
This article outlines the use of an IKA T 25 Easy Clean digital ULTRA-TURRAX® homogenizer in conjunction with a Mettler Toledo EVA V3 Karl Fischer titrator to determine the samples’ water content.
Four samples were analyzed, all of which would be difficult to measure without homogenization.

Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
The homogenizer acts as a blender and high-shear stirrer in this instance, helping to disperse or reduce samples that dissolve slowly or not at all.
Representative samples from different product categories were selected, including milk powder, moisturizer, almonds, and gummy candies.
Milk powder is easy to disperse but does not dissolve in the Karl Fischer solvent. Moisturizer does dissolve, but its oil-based components do not. In the case of these two samples, the homogenizer speeds up the dispersion process.
Gummy candies could be dissolved with assistance from the co-solvent formamide, but their dissolution would take more than 10 minutes. The use of a homogenizer considerably reduces the analysis time in this instance.
Almonds do not dissolve, however, and so must first be shredded into small pieces in order to allow water to be extracted into the KF solvent.

Figure 1. EVA V3 Karl Fischer Titrator assembly. Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Sample Preparation
Milk Powder
The milk powder did not require special sample preparation, and it was possible to determine the sample weight using the back-weighing technique.
Moisturizer Cream
A few grams of moisturizer were filled into a syringe to enable simpler weighing and dosing. This was done by pulling out the plunger and filling it from the backside, allowing the accurate addition of small sample sizes (0.02-0.04 g) into the KF cell. The back-weighing technique was used to determine the weight of the added sample.
Almonds
Prior to homogenizing, the whole almonds were chopped into small 3-4 mm diameter pieces. This can be done with either a kitchen blender or by hand with a sharp knife.
Sample weight was determined using the back-weighing technique.
Direct weighing was not used in this instance because oily crumbs would stick to the weighing boat or paper, and not being added to the cell would lead to incorrect results.
Gummy Candies
The gummy candies were also cut into smaller pieces to allow them to be shredded by the homogenizer. A knife was used to cut these into approximately five millimeter pieces.
Procedures
KF Concentration
It is advisable to determine the titrant concentration once daily before conducting any measurements using a certified water standard. For this application, the KF Concentration template T012 was selected, and the HYDRANAL™ water standard 10.0 was used.
KF Blank
Additional moisture may be introduced into the cell when running the homogenizer. A blank series is measured to compensate for this, with the homogenizer run at an identical speed and time as the sample analysis, without adding anything into the cell.
It is advisable to determine a new blank periodically to correct for environmental changes. A new blank should also be chosen every time the titration cell is taken apart and reassembled.
During the task creation, the provided method template (EVA0007) allows the user to select whether a blank measurement should be performed. The last blank determined will be used if no blank is measured.
A new blank value should be created if it is not predefined in the instrument settings. This is done by selecting ‘Setup > Values & Tables > Blank values’ in the instrument’s interface.
Titration
Samples were titrated using HYDRANAL™ Composite 5 one-component reagent with Methanol dry used as the solvent. In the case of the gummy candies, formamide was added as co-solvent in a 3:1 v/v methanol: formamide ratio in order to increase the gelatine’s solubility.
Titrations were performed with a focus on accuracy. The maximum start drift was set to 100 μg per minute. The KF cell was freshly set up for each sample type to avoid potential interference from leftover residues.
A series of three blanks followed by a series of six samples were measured in each task. Each measurement series was comprised of the following steps:
- Create and name a task from the EVA0007 method.
- Decide whether it is necessary to determine a blank.
- Enter the number of blanks and samples to be measured.
- Begin the task and wait for the KF cell to be ready. The button in the lower right corner will turn green when this is the case.
- Press the lower right button to begin the first measurement.
- If this is determined, a blank value is measured first. Otherwise, the operator will be asked to add the first sample.
- Samples are prepared in line with the Sample Preparation section before being measured.
Chemistry
ROH + SO2 + 3 RN + I2 + H2O → (RNH)SO4R + 2 (RNH)
Solutions and Reagents
Titrant: HYDRANAL™ Composite 5, c = 5 mg H2O/mL, one-component KF titrant
Solvents: HYDRANAL™ Methanol dry
Standard: HYDRANAL™ Water standard 10.0, water content: 10.0 mg/g = 1 %
Samples: Milk powder, moisturizer, almonds, and gummy candies were all purchased from a store and prepared as outlined in the Sample Preparation section.
Instruments and Accessories
- Karl Fischer Titrator EVA V3 (30869282)
- Analytical Balance, for example, XPR205 (30355411)
- Homogenizer adapter M24 d18 mm (30869297)
- IKA T 25 Easy Clean digital ULTRA-TURRAX® (0025002563) with S25N-18G dispersing tool (0000593400), available at: IKA.com

Figure 2. IKA T 25 Easy Clean digital ULTRA-TURRAX®. Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Results
Table 1. Four sample types were measured using different homogenizer settings. Each analysis consisted of 3 blank measurements followed by 6 sample determinations. The water content of the samples was corrected with the mean value of the blank measurements. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| Sample |
Homogenizer |
ID |
Blank [mg] |
Water content [%] |
Milk Powder
Sample size:
0.08 – 0.12 g |
Speed:
60 % (15 k rpm)
Time: 60 s |
1 |
0.246 |
4.613 |
| 2 |
0.194 |
4.632 |
| 3 |
0.156 |
4.531 |
| 4 |
- |
4.536 |
| 5 |
- |
4.544 |
| 6 |
- |
4.514 |
| mean |
0.199 |
4.562 |
| s |
0.045 |
0.049 |
| srel [%] |
22.742 |
1.063 |
Moisturizer
Sample size:
0.02 – 0.04 g |
Speed:
60 % (15 k rpm)
Time: 60 s |
1 |
0.131 |
77.645 |
| 2 |
0.111 |
79.342 |
| 3 |
0.082 |
84.350 |
| 4 |
- |
79.503 |
| 5 |
- |
78.905 |
| 6 |
- |
77.607 |
| mean |
0.108 |
78.600 |
| s |
0.025 |
0.916 |
| srel [%] |
22.812 |
1.166 |
Almonds
Sample size:
0.2 - 0.3 g |
Speed:
80 % (20k rpm)
Time: 150 s |
1 |
0.165 |
3.362 |
| 2 |
0.235 |
3.779 |
| 3 |
0.124 |
3.703 |
| 4 |
- |
3.573 |
| 5 |
- |
3.405 |
| 6 |
- |
3.547 |
| mean |
0.175 |
3.562 |
| s |
0.056 |
0.162 |
| srel [%] |
32.134 |
4.562 |
Gummy Candies
Sample size:
0.1 – 0.2 g |
Speed:
60 % (15 k rpm)
Time: 120 s |
1 |
0.343 |
15.793 |
| 2 |
0.336 |
15.880 |
| 3 |
0.180 |
15.729 |
| 4 |
- |
15.758 |
| 5 |
- |
15.611 |
| 6 |
- |
15.692 |
| mean |
0.286 |
15.744 |
| s |
0.092 |
0.091 |
| srel [%] |
32.184 |
0.580 |
This method achieved highly accurate and repeatable results for all sample types.
The almonds exhibited a comparatively poor relative standard deviation with approx. 4.6 %, but this is unsurprising due to the many challenges associated with the sample matrix. These results can be considered within expectations, considering the thick sample slurry used.
The gummy candies were reduced extremely quickly, completely dissolving with the help of the co-solvent formamide. This enabled highly repeatable measurements with a relative standard deviation just below 0.6 %.
Blank measurements appear to vary significantly, with relative standard deviations between 20 % and 30 %. This is due to the extremely low amount of water in all measurements, meaning that small changes led to large variations.
It is also important to note that running the homogenizer can cause splashes, which wash down parts of the inner cell walls. Without the homogenizer this would not occur, and it is likely that this has a considerable effect on deviations between measurements.
Remarks
A considerable amount of water adheres to the upper cell walls and the adapter plate if the cell has been freshly assembled, following manual cleaning. The cell can be washed down by manually turning on the homogenizer to avoid introducing this water into the first blank or sample measurement.
The cell is conditioned using the ‘KF Conditioning’ action before turning on the homogenizer for 10-15 seconds using the ‘Homogenizer’ operation. After washing the cell with conditioned solvent, the measurement can be started as normal.
The homogenizer’s speed and operating time are set in the method function ‘Homogenizer’ found within the Sample/Blank Sequence. The speed is entered as a percentage of the maximum speed achieved by the homogenizer. This speed is 25,000 rpm for the IKA T 25 easy clean digital homogenizer.
The sample solution was stirred for an additional 60 seconds after this to give the solvent sufficient time to extract as much water as possible from the sample matrix. This is particularly important when working with samples that do not dissolve, such as milk powder and almonds.
It is also important to note that samples that do not dissolve may not completely release all water until the end of the titration, potentially leading to a higher drift persisting for several minutes.
The maximum start drift was set to 100 μg per minute to avoid waiting for the drift to drop to a low enough value before commencing the next measurement.
Blank measurements are also a good indication of the whole system’s tightness. For example, determining a much higher blank than previous determinations indicates a leak in the KF cell assembly. If the blank remains high even after tightening all connections, it may be necessary to replace the O-rings.
Waste Disposal and Safety Measures
Safety googles, gloves, and a lab coat should be worn at all times while working with chemicals. It is also necessary to dispose of Karl Fischer waste as organic solvent waste.
Measured Values
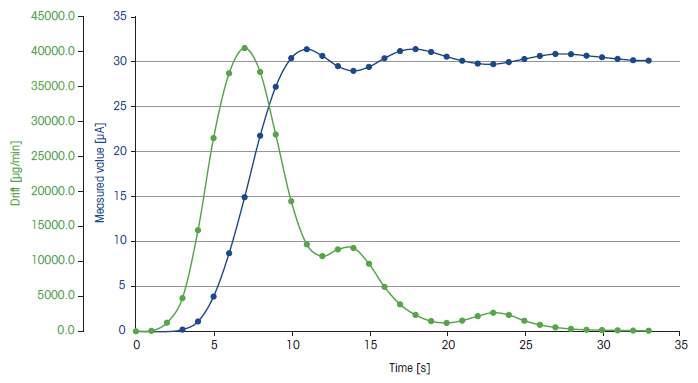
Figure 3. Typical titration curve obtained from the second milk powder measurement. Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Table 2. Measured values for the second milk powder measurement. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| Time [s] |
Volume [mL] |
Measured value [μA] |
Water [μg] |
Drift [μg/min] |
| 0 |
0.00000 |
-0.032737 |
0.000 |
0.0 |
| 1 |
0.00156 |
-0.032651 |
8.053 |
55.1 |
| 2 |
0.02763 |
-0.032914 |
142.626 |
1230.4 |
| 3 |
0.08744 |
0.187733 |
451.365 |
4748.6 |
| 4 |
0.25235 |
1.091048 |
1302.631 |
14462.9 |
| 5 |
0.41903 |
3.867030 |
2163.033 |
27650.9 |
| 6 |
0.58073 |
8.682095 |
2997.728 |
36916.3 |
| 7 |
0.70166 |
14.922188 |
3621.969 |
40543.3 |
| 8 |
0.75604 |
21.763436 |
3902.678 |
37110.1 |
| 9 |
0.76864 |
27.215173 |
3967.720 |
28166.0 |
| 10 |
0.77232 |
30.399321 |
3986.716 |
18615.9 |
| 11 |
0.79253 |
31.391583 |
4091.040 |
12437.7 |
| 12 |
0.83629 |
30.658465 |
4316.929 |
10762.6 |
| 13 |
0.88181 |
29.506024 |
4551.903 |
11709.7 |
| 14 |
0.90817 |
28.991656 |
4687.974 |
11925.7 |
| 15 |
0.91102 |
29.431950 |
4702.685 |
9667.9 |
| 16 |
0.91103 |
30.397169 |
4702.737 |
6356.8 |
| 17 |
0.91103 |
31.184912 |
4702.737 |
3858.1 |
| 18 |
0.91103 |
31.412914 |
4702.737 |
2339.8 |
| 19 |
0.91211 |
31.094970 |
4708.312 |
1456.6 |
| 20 |
0.91800 |
30.574734 |
4738.716 |
1197.7 |
| 21 |
0.92747 |
30.122334 |
4787.600 |
1531.2 |
| 22 |
0.94014 |
29.804441 |
4853.003 |
2170.4 |
| 23 |
0.94832 |
29.727706 |
4895.228 |
2659.9 |
| 24 |
0.94848 |
29.965079 |
4896.054 |
2340.0 |
| 25 |
0.94849 |
30.308728 |
4896.105 |
1516.0 |
| 26 |
0.94848 |
30.645751 |
4896.054 |
919.4 |
| 27 |
0.94848 |
30.866248 |
4896.054 |
557.6 |
| 28 |
0.94849 |
30.838862 |
4896.105 |
338.2 |
| 29 |
0.94888 |
30.683563 |
4898.119 |
215.6 |
| 30 |
0.94900 |
30.499780 |
4898.738 |
161.5 |
| 31 |
0.94926 |
30.319842 |
4900.080 |
127.2 |
| 32 |
0.94936 |
30.173383 |
4900.596 |
98.4 |
| 33 |
0.94936 |
30.127142 |
4900.596 |
73.5 |
Method
General Settings. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| . |
. |
| Name |
KF vol homogenizer |
| ID |
EVA0007 |
| Compatibility |
Titration |
| Model compatibility |
V3 |
| Method type |
KF Volumetric |
| SOP |
NO |
| Task comment |
NO |
Configuration. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| Analysis |
|
| Analyze more than one sample |
YES |
| Initial sequence |
NO |
| Final sequence |
NO |
| Determine blank |
YES |
| Open series |
NO |
| Analysis start |
Manual |
| Number of samples |
3 |
| Create statistics |
YES |
| Activate ‘KF conditioning’ after method ends |
YES |
| KF cell |
KF cell 1 |
| Category |
Volumetric (large) |
| Unit for drift |
μg/min |
| Work with solvent exchange |
YES |
| KF pump |
dPump KF 1 |
| Start criteria |
Absolute drift values |
| Min. start drift |
0.0 μg/min |
| Max. start drift |
100.0 μg/min |
| Blank |
|
| Blank measurement |
Decide at task start |
| Open series |
NO |
| Number of blanks |
3 |
| Create statistics |
YES |
| Blank calculation (mean value) |
R2 |
| Blank “B” |
Blank value 1 |
| Unit “B” |
mg |
| Result limits |
NO |
| Live View |
|
| Displayed results (Sample) |
3 |
| Field 1 |
R1 |
| Displayed results (Blank) |
1 |
| Field 1 |
R2 |
| Analysis graph: Horizontal axis |
Time |
| Analysis graph: Vertical axis |
Measured value |
| Additional curve |
Drift |
| Conditioning graph: Horizontal axis |
Time |
| Conditioning graph: Vertical axis |
Drift |
Blank Sequence. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| 1 Drift (Determination – online) |
|
|
| Drift determination |
|
YES |
| Determine online (during conditioning) |
|
YES |
| 2 Blank (Addition) |
|
|
| Prompt for blank addition |
|
NO |
| 3 Homogenizer |
|
|
| Homogenizer |
|
Homogenizer 1 |
| Speed |
|
60 % |
| Duration |
|
60 seconds |
| 4 Titration (KF Vol) |
|
|
| Resources |
|
|
| Titrant |
Titrant |
Titrant 1 |
|
Nominal concentration |
5 mg/mL |
| Sensor |
Sensor |
dSens M143 |
|
Category |
Polarized |
| Stirrer |
Stirrer |
Stirrer 1 |
|
Category |
Magnetic |
|
Stir speed |
35 % |
| Titration |
|
|
| Preparation |
Stir before titration |
60 seconds |
| Control |
Control focus |
Accuracy |
|
Indication |
Amperometric |
|
Unit |
μA |
|
Potential (Upol) |
100 mV |
|
Set current |
30 μA |
|
Cautious mode |
NO |
| Termination |
Type |
Drift stop relative |
|
Drift relative |
25.0 μg/min |
|
Delay |
0 seconds |
|
Min. time |
10 seconds |
|
Max. time |
∞ seconds |
|
At Vmax |
10 mL |
| 5 Result R2: Content |
|
|
| Formula type |
Fixed |
|
| Result name |
Content |
|
| Formula |
(VEQ*CONC-TIME*DRIFT/1000) |
|
| Unit |
mg |
|
| Decimal places |
3 |
|
| Result limits |
NO |
|
Sample Sequence. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| 1 Drift (Determination – online) |
|
| Drift determination |
|
YES |
| Determine online (during conditioning) |
|
YES |
| 2 Sample (Addition) |
|
|
| Prompt for sample addition |
|
YES |
| Sample detection |
|
No |
| Prompt for sample size |
|
YES |
| 3 Homogenizer |
|
|
| Homogenizer |
|
Homogenizer 1 |
| Speed |
|
60 % |
| Duration |
|
60 seconds |
| 4 Titration (KF Vol) |
|
|
| Resources |
|
|
| Titrant |
Titrant |
Titrant 1 |
|
Nominal concentration |
5 mg/mL |
| Sensor |
Sensor |
dSens M143 |
|
Category |
Polarized |
| Stirrer |
Stirrer |
Stirrer 1 |
|
Category |
Magnetic |
|
Stir speed |
35 % |
| Titration |
|
|
| Preparation |
Stir before titration |
60 seconds |
| Control |
Control focus |
Accuracy |
|
Indication |
Amperometric |
|
Unit |
μA |
|
Potential (Upol) |
100 mV |
|
Set current |
30 μA |
|
Cautious mode |
NO |
| Termination |
Type |
Drift stop relative |
|
Drift relative |
25.0 μg/min |
|
Delay |
0 seconds |
|
Min. time |
0 seconds |
|
Max. time |
∞ seconds |
|
At Vmax |
10 mL |
| 5 Result R1: Content |
|
|
| Formula type |
Editable |
|
| Result name |
Content |
|
| Formula |
(VEQ*CONC-TIME*DRIFT/1000-B[Blank value 1])*(0.1/m) |
|
| Unit |
% |
|
| Decimal places |
3 |
|
| Result limits |
NO |
|
References and Further Reading
- Application notes M316-M322 for the previous generation instruments (V30, V30S, T7 and T9) can be found in the application library: Applications Library - METTLER TOLEDO (mt.com)
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Mettler Toledo.

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Mettler-Toledo - Titration.
For more information on this source, please visit Mettler-Toledo - Titration.