Volumetric Karl Fischer (KF) titration is the ideal choice for quickly and accurately determining water content across a large quantity of samples. The titration is based on the reaction of water with iodine, sulfur dioxide, a base, and a short chain alcohol, which is also usually the reaction’s solvent.
The KF approach can be applied to solids, liquids, and gases as long as the water inside the sample can be released from the sample matrix and then titrated by the KF reagent.
Solid samples that don’t dissolve in the KF solvent should release their water before they can be processed through titration. Extracting the water content into the solvent can take several minutes to multiple hours and is heavily dependent on the sample matrix and its granularity, i.e. the sizes of the individual sample pieces from which water is extracted.
External extraction eliminates this demanding step, carrying it out in an external vessel and allowing the instrument to take other measurements. When the water has been removed from the sample solution, it can then be loaded into the KF cell for rapid and precise determination of the water quantity.
This article describes the external extraction process and demonstrates how a METTLER TOLEDO EVA V3 KF titrator can be used to calculate the water content of Rooibos tea with precision.

Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Introduction
Extracting water from an insoluble, solid sample into the KF solvent can take just a few minutes in some circumstances and hours in others. Extraction is often carried out in an external vessel to ensure the instrument is not blocked throughout the whole process.
While the KF solvent can be used for extraction, any solvent that can take up water may be used. This heightens the method’s versatility and accuracy, as the solvent choice can be customized for each sample.
Here, the water content of Rooibos tea is calculated via a METTLER TOLEDO EVA V3 Karl Fischer titrator using the external extraction approach. In this case, Methanol dry is an appropriate solvent for extraction purposes, and the samples are titrated with a 5.0 mg/mL one-component KF titrant.
The water content of the extraction solvent is assessed and stored as a blank value. This content is expected to be very small, so the ‘Accuracy’ control focus is used, and ‘Cautious mode’ is switched on. For the most accurate results, all measurements should be carried out with identical settings. As such, the KF Concentration and sample measurements additionally use ‘Accuracy’ focus as well as the ‘Cautious mode’.
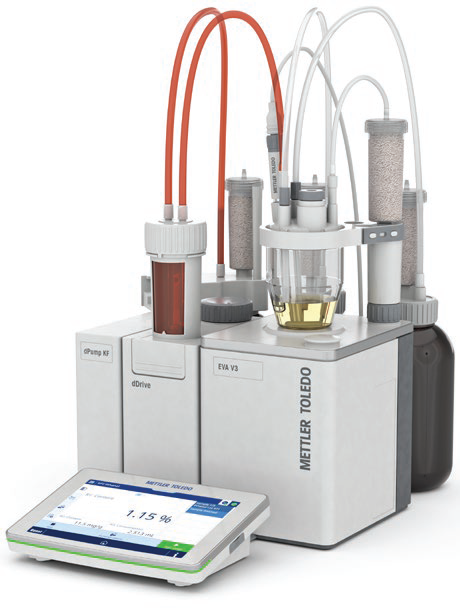

Figure 1. EVA V3 Karl Fischer Titrator assembly. Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Procedures
KF Concentration:
Calculating titrant concentration once per day before taking any sample measurements using a certified water standard is recommended. To do so, the KF Concentration template T012 is gently modified by switching on the ‘Cautious mode’ (Sequence tab > Titration (KF vol) > Titration tab > Control). A 10.0 mg/g water standard is used as the reference standard and assessed three times.
Titration:
Water from the tea is extracted into the methanol, and the extraction solution’s water content is then calculated. Multiple parameters are required to determine the tea's actual water content.
- The extraction solvent’s mass (msol)
- The extraction solvent’s water content (Blank B)
- The extract sample’s mass (mext)
- The extraction solution’s mass injected into the KF cell (m)
Using these values, the water content R of the sample (in %) can be determined via the formula:
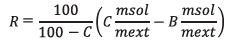
Where C is the water content (in %) of the extraction solution given by the formula:
C = (VEQ*CONC-TIME*DRIFT/1000)*(0.1/m)
and B is the blank value (in %), which is determined prior to the determination of the extraction solution.
The full process involves several steps:
- Prepare two clean bottles (or flasks, vials, etc.) that can be sealed with either a septum or stopper.
- Label one of the bottles with “Sample” and tare it on the balance.
- Add ~ 50 mL of methanol and note down the added methanol’s weight as ‘msol’.
- Label the second bottle with “Blank” and add approximately the same quantity of methanol, then close the bottle. It is not important to calculate the exact weight in this case.
- Weigh about 4.0 g of Rooibos tea and note down the weight as ‘mext’. Add the tea to the Sample bottle.
- Ensure both bottles are sealed tightly and wait at least one hour for the solvent to extract all water. To accelerate the extraction process, shake the bottle occasionally and stir its contents on a stir plate.
- Create a task from the external extraction approach T015 and choose the task name, number of samples, and number of blanks.
- Enter the mass which was written down as msol into the field ‘Solvent weight’ and the weight marked as mext into the field ‘Extr. sample weight’.
- Begin the task and wait for the KF cell to be ready.
- While waiting, rinse away the adhered moisture from the inner walls of a 10 mL syringe: Draw around 3 mL of methanol from the Blank bottle into the syringe, then pull the plunger back completely. Swirl the solvent inside the syringe for a few seconds, then place it into the solvent waste. Next, refill the syringe with 10 mL of methanol from the Blank bottle.
- When the cell is ready for the next step with blank measurements, administer 1-3 mL of solvent each time, according to the water content. The injected solvent’s mass is calculated via the back-weighing approach.
- Finally, the extraction solution from the Sample bottle will be assessed using the same process as the blank determinations.
- The tea’s water content is determined and delivered as the main result.
Chemistry
ROH + SO2 + 3 RN + I2 + H2O → (RNH)SO4R + 2 (RNH)I
Solutions and Reagents
- Titrant: HYDRANAL™ Composite 5, c = 5 mg H2O/mL, one-component KF titrant
- Solvents: HYDRANAL™ Methanol dry
- Standard: HYDRANAL™ Water standard 10.0, water content: 10.0 mg/g = 1 %
- Samples: Rooibos tea was store bought.
Instruments and Accessories
- Karl Fischer Titrator EVA V3 (30869282)
- Analytical Balance, e.g., XPR205 (30355411)
- 10 mL syringes (00071482)
- 2 sealable vessels (bottles, flasks, vials, etc.)

Figure 2. Example of two extraction bottles. Left: Blank bottle containing methanol. Right: Sample bottle with the added Rooibos tea and msol and mext written directly onto it. Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Results
Table 1. Water content of the methanol blank. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
|
Water content Blank [%] |
Blank size [g] |
| 1 |
0.0085 |
2.3549 |
| 2 |
0.0104 |
2.2768 |
| 3 |
0.0093 |
2.3083 |
| mean |
0.0094 |
- |
| s |
0.0010 |
- |
| srel |
10.148 |
- |
Table 2. Water content of the Rooibos tea. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
|
Water content Sample [%] |
Sample size [g] |
| 1 |
6.654 |
0.5839 |
| 2 |
6.658 |
0.6384 |
| 3 |
6.648 |
0.7039 |
| 4 |
6.643 |
0.8614 |
| 5 |
6.647 |
0.7783 |
| 6 |
6.649 |
0.8368 |
| mean |
6.650 |
- |
| s |
0.005 |
- |
| srel |
0.076 |
- |
Using methanol dry as a solvent resulted in a very low blank value calculated. As a result, repeated measurements can lead to sizable relative standard deviations, as tiny variations in measurements will produce significant variances across results.
For Rooibos tea, a water content of 6.65 % was calculated with an exceptionally low relative standard deviation of 0.076 %, suggestive of high repeatability.
While the key focus is on obtaining the most accurate results, titration times spanning 81 to 97 seconds also demonstrate that a precise analysis can be conducted in only a few minutes.
Remarks
- To ensure that one hour was a reasonable amount of time for extraction purposes, an identical sample solution was assessed again 24 hours after the extraction. In this time, the solvent’s blank value increased to 0.0129 % and the tea’s water content was calculated at 6.738 %. Here, one hour was sufficient for extracting 98.7 % of the water content as opposed to extracting for 24 hours.
- Extraction time can be reduced by putting the extraction vessel in a sonicator (ultrasonic cleaner) or heating it gently in a water bath. However, these options should be investigated on a sample-by-sample basis.
Waste Disposal and Safety Measures
Always wear safety goggles, a lab coat, and gloves when using chemicals. Karl Fischer waste products should be disposed of as organic solvent waste.
Measured Values
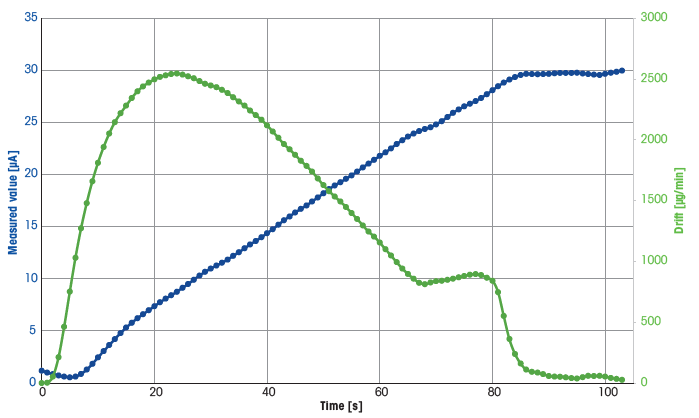
Figure 3. A typical titration curve, taken from the first measurement of the extraction solution. Image Credit: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
Table 3. Titration data for the for the first measurement of the extraction solution. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| Time [s] |
Volume [mL] |
Measured value [μA] |
Water [μg] |
Drift [μg/min] |
| 0 |
0 |
1.184848 |
0 |
0 |
| 1 |
0.00006 |
1.002622 |
0.295 |
2.3 |
| 2 |
0.00126 |
0.848009 |
6.204 |
53.1 |
| 3 |
0.00386 |
0.717578 |
19.007 |
211.9 |
| 4 |
0.00768 |
0.606138 |
37.816 |
463.1 |
| 5 |
0.01247 |
0.547025 |
61.402 |
751.1 |
| 6 |
0.01795 |
0.615915 |
88.386 |
1030.0 |
| 7 |
0.02391 |
0.862672 |
117.733 |
1272.6 |
| 8 |
0.03036 |
1.283786 |
149.493 |
1479.7 |
| 9 |
0.03725 |
1.833985 |
183.419 |
1659.5 |
| 10 |
0.04439 |
2.451424 |
218.576 |
1811.7 |
| … |
… |
… |
… |
… |
| 93 |
0.44779 |
29.75457 |
2204.918 |
46.8 |
| 94 |
0.44792 |
29.76553 |
2205.558 |
40.0 |
| 95 |
0.44803 |
29.77875 |
2206.100 |
37.5 |
| 96 |
0.44843 |
29.70753 |
2208.069 |
48.1 |
| 97 |
0.44856 |
29.65225 |
2208.709 |
58.6 |
| 98 |
0.44879 |
29.59659 |
2209.842 |
57.5 |
| 99 |
0.44893 |
29.56767 |
2210.531 |
58.3 |
| 100 |
0.44905 |
29.67253 |
2211.122 |
52.5 |
| 101 |
0.44906 |
29.77894 |
2211.171 |
41.4 |
| 102 |
0.44917 |
29.87589 |
2211.713 |
33.9 |
| 103 |
0.44916 |
29.97887 |
2211.664 |
26.6 |
Method – External Extraction
General Settings. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| . |
. |
| Name |
KF vol ext. extraction (%) |
| ID |
T015 |
| Compatibility |
Titration |
| Method type |
KF Vol External Extraction |
| SOP |
NO |
| Task comment |
NO |
Configuration. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| Analysis |
|
| Analyze more than one sample |
YES |
| Initial sequence |
NO |
| Final sequence |
NO |
| Open series |
NO |
| Analysis start |
Manual |
| Number of samples |
Six |
| Create statistics |
YES |
| Group samples for statistics |
NO |
| Activate ‘KF conditioning’ after method ends |
YES |
| KF cell |
KF cell 1 |
| Category |
Volumetric (large) |
| Unit for drift |
μg/min |
| Work with solvent exchange |
YES |
| KF pump |
dPump KF 1 |
| Start criteria |
Absolute drift values |
| Min. start drift |
0.0 μg/min |
| Max. start drift |
25 μg/min |
| Blank |
|
| Blank measurement |
Always |
| Open series |
NO |
| Number of blanks |
Three |
| Create statistics |
YES |
| Blank calculation (mean value) |
R2 |
| Blank “B” |
Blank value 1 |
| Unit “B” |
% |
| Result limits |
NO |
| Live View |
|
| Displayed results (Sample) |
1 |
| Field 1 |
R1 |
| Displayed results (Blank) |
1 |
| Field 1 |
R2 |
| Analysis graph: Horizontal axis |
Time |
| Analysis graph: Vertical axis |
Measured value |
| Additional curve |
Drift |
| Conditioning graph: Horizontal axis |
Time |
| Conditioning graph: Vertical axis |
Drift |
Blank Sequence. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| 1 Drift (Determination – online) |
|
|
| Drift determination |
|
YES |
| Determine online (during conditioning) |
|
YES |
| 2 Blank (Addition) |
|
|
| Prompt for blank addition |
|
YES |
| Blank detection |
|
No |
| Prompt for blank size |
|
YES |
| 3 Titration (KF Vol) |
|
|
| Resources |
|
|
| Titrant |
Titrant |
Titrant 1 |
|
Nominal concentration |
5 mg/mL |
| Sensor |
Sensor |
dSens M143 |
|
Category |
Polarized |
| Stirrer |
Stirrer |
Stirrer 1 |
|
Category |
Magnetic |
|
Stir speed |
35 % |
| Titration |
|
|
| Preparation |
Stir before titration |
10 seconds |
| Control |
Control focus |
Accuracy |
|
Indication |
Amperometric |
|
Unit |
μA |
|
Potential (Upol) |
100 mV |
|
Set current |
30 μA |
|
Cautious mode |
YES |
| Termination |
Type |
Drift stop relative |
|
Drift relative |
25.0 μg/min |
|
Delay |
0 seconds |
|
Min. time |
0 seconds |
|
Max. time |
∞ seconds |
|
At Vmax |
10 mL |
| 4 Result R2: Blank value |
|
|
| Formula type |
Fixed |
|
| Result name |
Blank value |
|
| Formula |
(VEQ*CONC-TIME*DRIFT/1000)*(0.1/m) |
| Unit |
% |
|
| Decimal places |
4 |
|
| Result limits |
NO |
|
Sample Sequence. Source: Mettler-Toledo - Titration
| 1 Drift (Determination – online) |
|
|
| Drift determination |
|
YES |
| Determine online (during conditioning) |
|
YES |
| 2 Sample (Addition) |
|
|
| Prompt for sample addition |
|
YES |
| Sample detection |
|
No |
| Prompt for sample size |
|
YES |
| Prompt for external extraction weight |
|
NO |
| 3 Titration (KF Vol) |
|
|
| Resources |
|
|
| Titrant |
Titrant |
Titrant 1 |
|
Nominal concentration |
5 mg/mL |
| Sensor |
Sensor |
dSens M143 |
|
Category |
Polarized |
| Stirrer |
Stirrer |
Stirrer 1 |
|
Category |
Magnetic |
|
Stir speed |
35 % |
| Titration |
|
|
| Preparation |
Stir before titration |
10 seconds |
| Control |
Control focus |
Accuracy |
|
Indication |
Amperometric |
|
Unit |
μA |
|
Potential (Upol) |
100 mV |
|
Set current |
30 μA |
|
Cautious mode |
YES |
| Termination |
Type |
Drift stop relative |
|
Drift relative |
25 μg/min |
|
Delay |
0 seconds |
|
Min. time |
0 seconds |
|
Max. time |
∞ seconds |
|
At Vmax |
10 mL |
| 4 Result R1: External extraction |
|
|
| Formula type |
Fixed |
|
| Result name |
External extraction |
|
| Formula |
100/(100-(VEQ*CONCTIME*DRIFT/1000)*(0.1/m))*(((VEQ*CONC-TIME*DRIFT/1000)*(0.1/m))*msol/mext-B*msol/mext) |
| Unit |
% |
|
| Decimal places |
3 |
|
| Result limits |
NO |
|
References and Further Reading
Titration Application notes developed for V30, V30S, T7 and T9:
- Determination of the water content in tobacco by external extraction / M305
- Water Content in Charcoal by Karl Fischer Titration / M817

This information has been sourced, reviewed, and adapted from materials provided by Mettler-Toledo - Titration.
For more information on this source, please visit Mettler-Toledo - Titration.