Xradia Synchrotron solutions from ZEISS allow users to avoid expensive and laborious in-house development by bringing nanoscale X-Ray imaging to the synchrotron facility. The adjustable and ultra-bright X-Ray beams that are available at present synchrotron facilities are integrated with proprietary X-Ray optics and a well-known 3D X-Ray microscopy platform.
Having a range of contrast settings, it is possible for users to obtain rapid and non-destructive 3D imaging with a resolution of <30 nm. The 3D imaging microscopes of the Xradia Synchrotron series encompass an extensive energy range from mild to hard X-Rays.
Highlights
Xradia 800 Synchrotron: Hard X-Ray Nanotomography
With 3D tomographic imaging using X-Rays, comprehensive volumetric data on internal structures can be obtained without the need for cutting or sectioning at the region of interest.
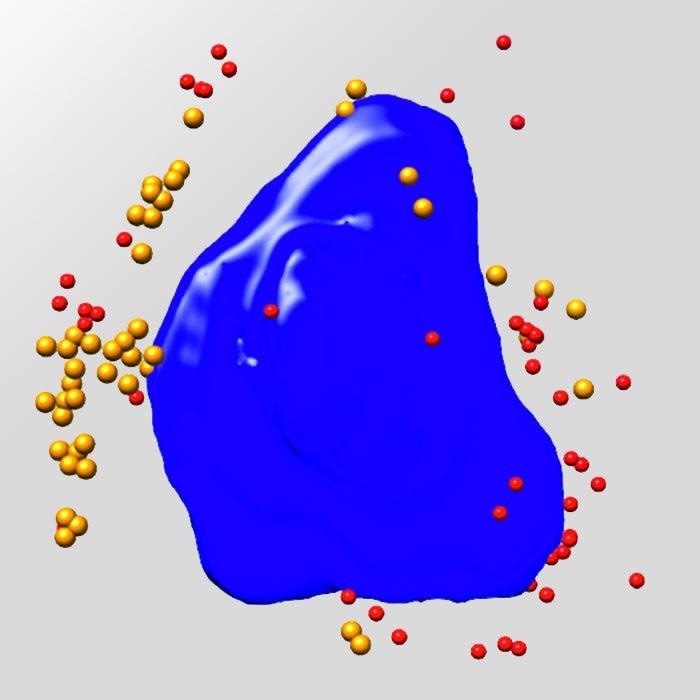
The Xradia 800 Synchrotron, functioning in the 5–11 keV energy range, has the potential to photograph a broad range of samples with a resolution of <30 nm. This includes catalysts, battery and fuel cell electrodes, and hard and soft tissue.
Sophisticated methods, such as XANES spectro-microscopy for 3D chemical mapping and in situ imaging on the Xradia 800 Synchrotron, help to examine materials in real-world settings.
Xradia 825 Synchrotron: Soft X-Ray Nanotomography
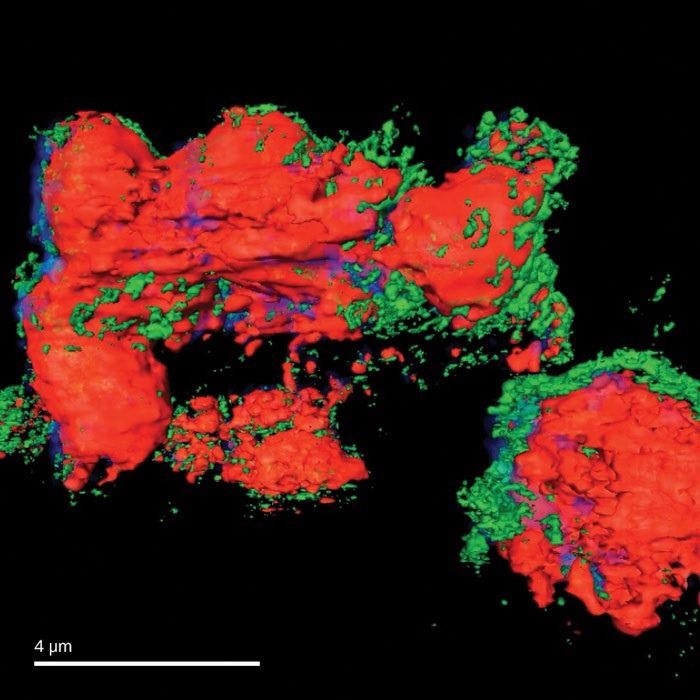
3D tomographic imaging in the soft X-Ray range, which consists of the water window up to 2.5 keV is suitable for the structural imaging of complete tissues and cells.
Cryogenic sample management enables users to image in a hydrated, frozen condition, thereby decreasing radiation damage and retaining the material as near to its natural state as possible. Also, chemical state mapping of organic and inorganic materials, as well as imaging of magnetic domains, are utilized.
Nickel Battery. Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials
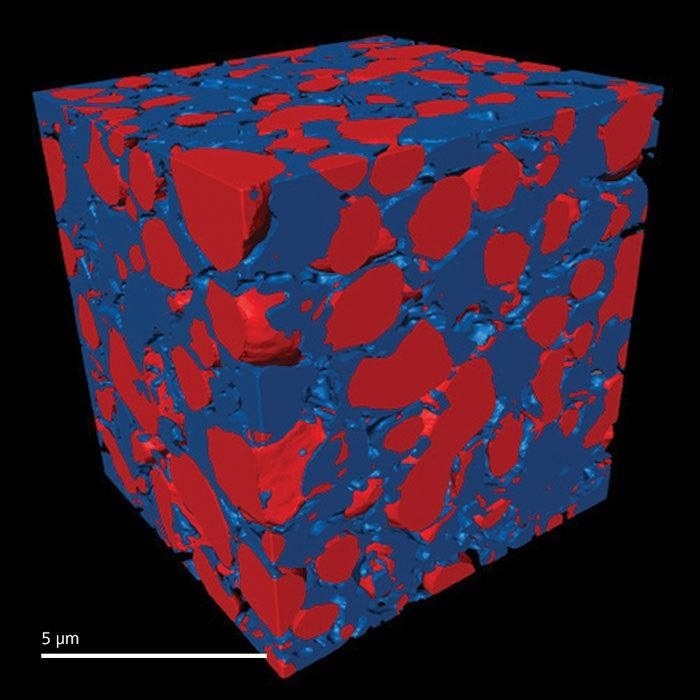
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell. Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials
Virus-infected Ptk2 Cell. Image Credit: Carl Zeiss Raw Materials
Benefits
Thanks to the ZEISS-proven synchrotron systems, users can invest time and energy into the study instead of expensive and laborious in-house development.
With the help of proven 3D X-Ray microscopy platforms, it is possible for users to choose the system that best suits particular research requirements.
Xradia 800 Synchrotron: Hard X-Ray Nanotomography
- With the help of the XANES spectroscopy, it is possible to identify the oxidation states of electrochemical catalysts or devices
- With exceptional picture quality and throughput, users can experiment with advanced methods and examine a wide range of samples in situ to better understand the impact of real-world operating circumstances
- Use non-destructive 3D tomographic imaging with a resolution ranging <30 nm for elaborate volumetric data in the absence of sectioning or cutting at the region of interest
Xradia 825 Synchrotron: Soft X-Ray Nanotomography
- Users can image the structure of entire cells and tissues while reducing the impact of radiation damage by adopting cryogenic sample handling
- Correlate to optical fluorescence microscopy for structure and function imaging
- Utilize the so-called “water window” energy range to make high-contrast images of organic objects in their natural and wet surroundings