The Nanophoton RAMANwalk is a confocal Raman microscope based on galvanoscanner technology. By using this technology, it can move the laser point across a sample at a much faster speed than conventional systems. By using stochastic processes and information theory, samples can be scanned at imaging speeds five to ten times faster than traditional methods. This efficiency makes it ideal for rapid screening. This video showcases the use of this approach:
Raman Point Scanning
Demonstration of Laser Point Scanning. Video Credit: Bruker Optics
RAMANwalk Key Features:
RAMANwalk microscope with laser class 1 safety housing. Image Credit: Bruker Optics
The Random Walk Algorithm explained
Introducing the Basics
This illustration compares laser movement in a Random Walk approach (right) versus a traditional scanning method (left). Instead of following a fixed path, the algorithm intelligently adjusts based on detected Raman signals. When it identifies a signal, it immediately explores nearby areas until the intensity shifts or fades. Signal thresholds - such as S/N ratio, peak height, or peak area - guide this process. The system then calculates the next optimal scanning point, making it significantly more efficient than conventional point-by-point scanning. This results in faster, smarter sample analysis.
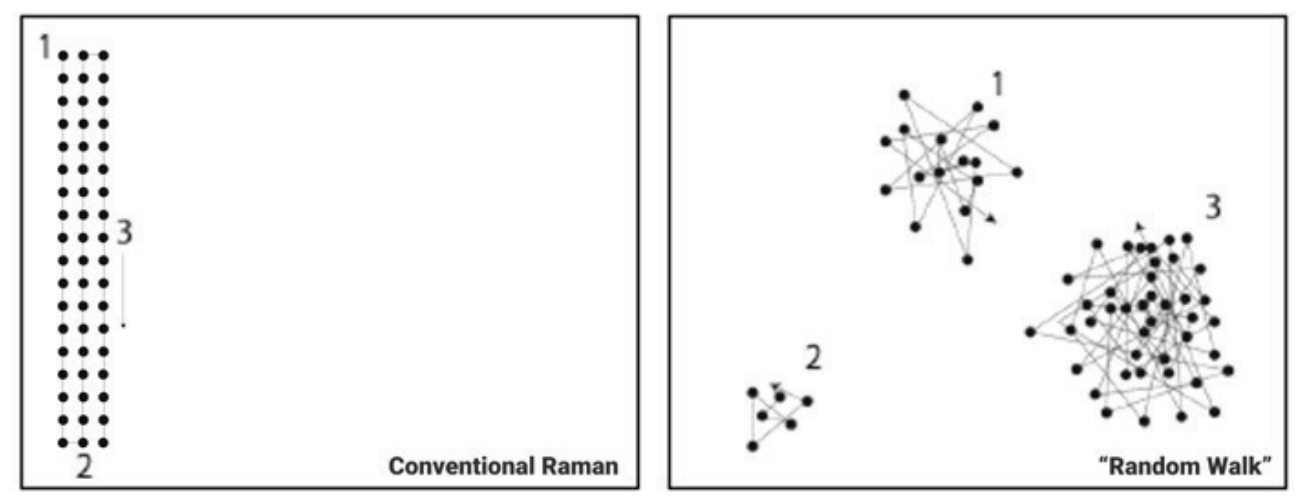
Image Credit: Bruker Optics
Visualizing the principle with a benchmark sample
This first benchmark example demonstrates the imaging of sparsely distributed plastic beads on a glass surface using point-mode Raman imaging. In the bottom image, you can see the visual image (A), the conventional Raman image after 10 minutes (B), and the Random Walk Raman image after 10 minutes (C). Clearly, (C) provides a far more representative picture of the sample. However, we can enhance this preview even further by interpolating the data already collected.
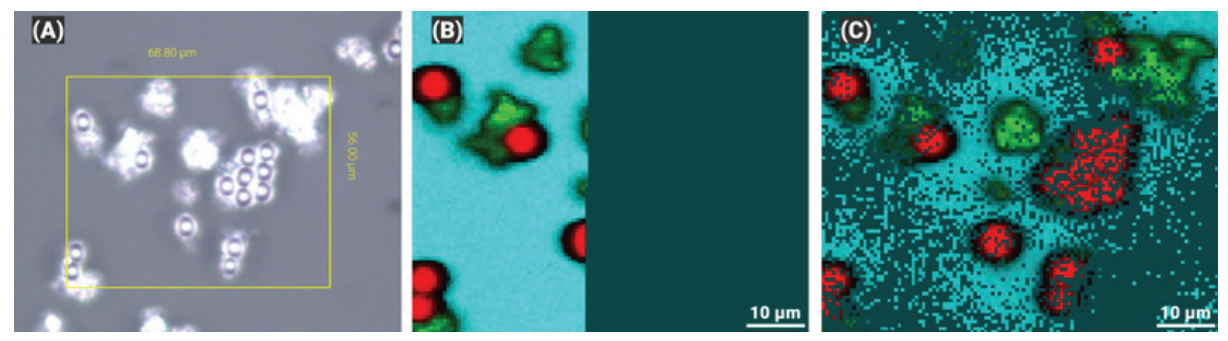
Image Credit: Bruker Optics
Transferring the approach to a real-world sample
This example was taken from the analysis of a barley grain tissue section. Figure 4 shows red, little pockets of starch within the grain tissue. The left image was interpolated and exported from the Random Walk measurement after 5 minutes, while the right image was run to completion. The interpolated image, after only 1/4 of the complete imaging time, already provides a very accurate representation of the final result
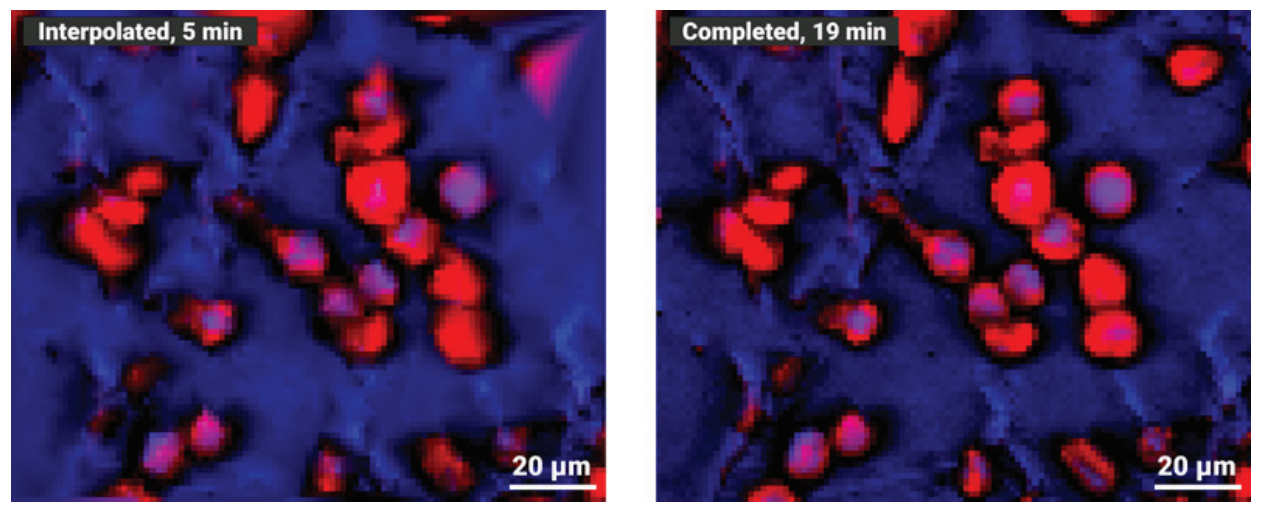
Image Credit: Bruker Optics
For quick analytical tasks where ultra-fine detail isn’t required or when selecting a region of interest for deeper Raman imaging, the RAMANwalk saves valuable time. It works smarter, not harder.