Bioadhesives are currently a research focus in the biomedical industry. The need for these adhesives and drug delivery systems has been facilitated in part by an aging population and increasing healthcare costs. The term bioadhesion refers to the phenomenon wherein two materials, one of which is biological, are attached to each other for prolonged periods by interfacial tailoring.
These materials have the advantages of biocompatibility, biodegradability, and non-toxicity over conventional synthetic adhesives. Additionally, these materials possess a large molecular weight. They have been explored for use in drug delivery, wound repair, aiding hemostasis, and many soft- and hard-tissue applications.
However, despite their advantages, the development of functional bioadhesives is hindered by several challenges in their design, with many available adhesives being static in nature. The need for intelligent materials has driven research in the field.
Smart Bioadhesives
Designing bioadhesives with enhanced functionality is a challenging area of research. Studies have recently reported the development of bioadhesives with antimicrobial properties and self-healing characteristics.
Materials with stimuli-responsive behaviors have recently been introduced into the field of biomedicine. Stimuli that smart bioadhesives respond to include UV light, pH, temperature, ions, magnetic and electrical fields, solvents, biomolecules, mechanical stress, and redox conditions.
These types of biocompatible and biodegradable non-toxic adhesives are useful for the controlled release of drugs and therapeutics, wound healing, and non-invasive repair of implantable devices in the body. Easy to control and inexpensive, they can change their adhesive behavior and performance in response to changes in physiological conditions. Thus, they can promote more effective treatment processes, providing a powerful tool for clinicians to improve the medical outcome of interventions.
The Study
The study has provided a comprehensive review of the current advances in the field of smart bioadhesive research. More than two hundred papers have been reviewed in the new research, covering several aspects of research and technological advances over the past few decades.
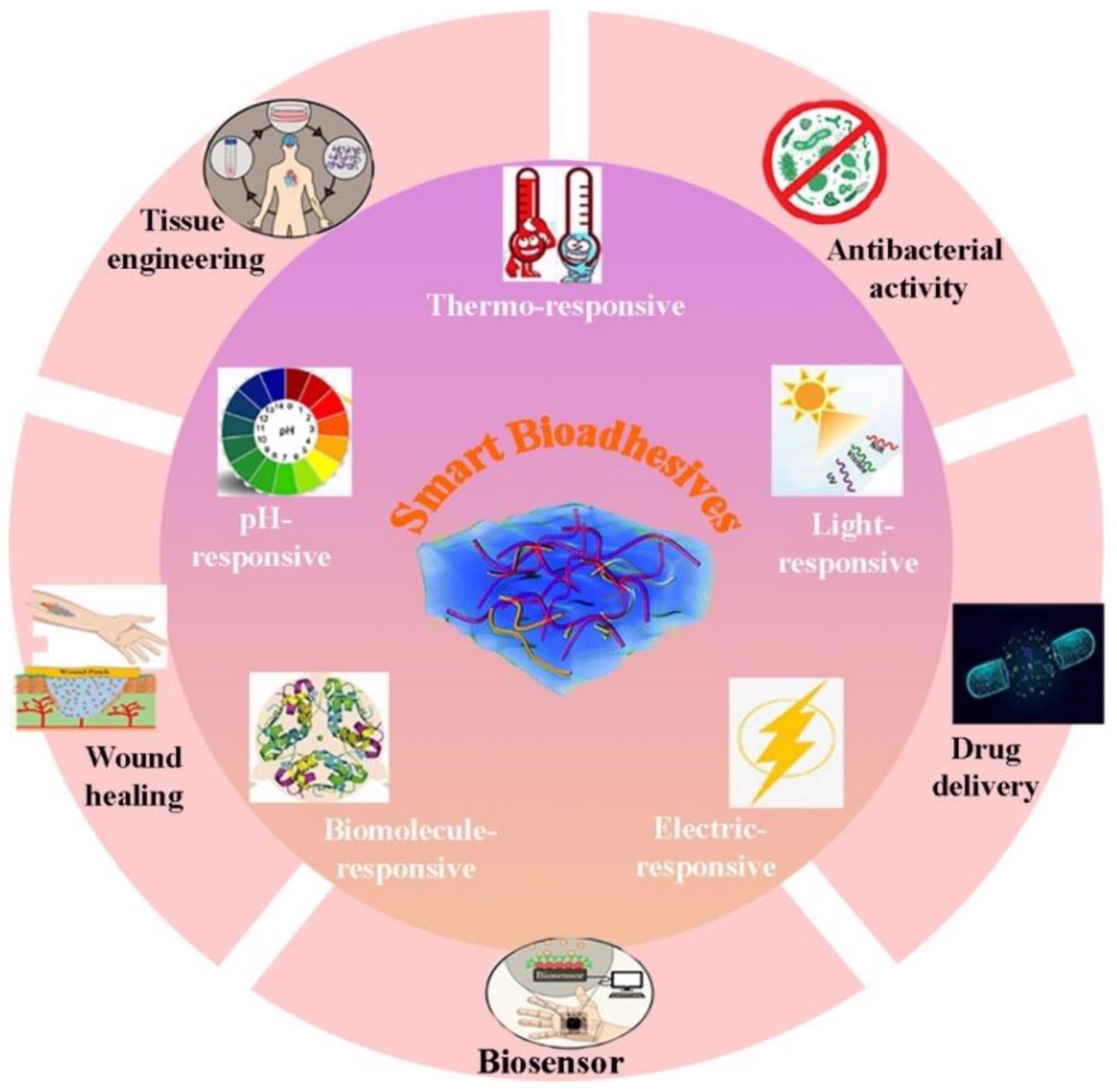
Schematic representation of various types of intelligent bioadhesives applied for different biomedical applications. Image Credit: Khadem, E et al., Polymers
A review of mono bioadhesives has not been included in the current review paper. Current papers have also extensively classified the various materials that are used, as well as application routes for drug delivery, amongst other pertinent areas of research. Despite there being a significant body of research, according to the authors there is a knowledge gap when it comes to the development of multifunctional bioadhesives for medical applications.
Compared to previous research in the field, the paper provides a comprehensive overview of current smart adhesives, limitations, and future challenges and perspectives for the development of advanced, smart bioadhesives. Recent innovative strategies for manufacturing stimuli-responsive materials that can respond to external stimuli and possess self-healing and shape-changing abilities have been summarized by the authors.
The review has highlighted and discussed the principal criteria for these innovative materials. Furthermore, the cutting-edge applications of these adhesives have been studied, such as tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound repair.
Conclusions, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
The review has concluded that the field of bioadhesives offers several advantages for biomedicine, and the recent development of stimuli-responsive materials has broadened the scope of these materials, facilitating the development of smart, responsive adhesives. The development of these materials provides opportunities for enhancing tissue engineering, wound repair, and the success of targeted, controlled drug delivery strategies.
However, there are still several challenges that must be overcome in research to realize the potential of these intelligent materials. Primarily is the need for low-cost, facile processes for manufacturing bioinspired structures and introducing stimuli-responsive behavior. Currently, due to scaling issues, materials are mostly limited to the laboratory.
Secondly, smart hydrogels, which have been proposed as materials for this purpose, are limited due to their performance outside an aqueous environment, hindering applications such as reconstructing damaged muscle tissue. Further issues exist with balancing structural performance, adhesion, and biodegradability. Moreover, challenges exist with drug delivery monitoring, which hinders the commercial applications of these biomaterials.
Fabricating cytocompatible materials for use as adhesives in drug delivery and tissue engineering also requires the careful evaluation of several factors. These include inflammation, degradability, reaction time, and the host’s immune response. Whilst many challenges currently exist in the field, the review has provided a wealth of information on current progress.
The authors have stated that they hope to stimulate an interdisciplinary approach in the future to help further promote the development of these smart materials.
Further Reading
Khadem, E et al. (2022) Cutting-Edge Progress in Stimuli-Responsive Bioadhesives: From Synthesis to Clinical Applications Polymers 14(9) 1709 | mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/14/9/1709
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.