MAT3D-XL seeks to overcome the technical challenges of the sector through new recycled or renewable compounds and advanced thermal technologies
AIMPLAS has developed several functional demonstrators that showcase the potential of the new materials and technologies applied, such as an automotive spoiler and parts for street furniture and interior design
The project is being carried out in collaboration with Ford, Molder Disnova and Plàstic Preciós La Safor, and is funded by IVACE+i and the ERDF
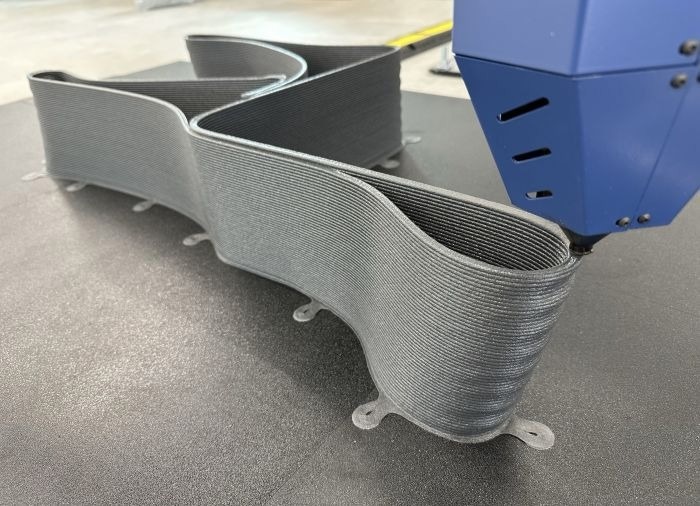 Image Credit: AIMPLAS
Image Credit: AIMPLAS
Large-format additive manufacturing has established itself as a key technology in demanding industrial sectors such as automotive and urban design, thanks to its ability to manufacture large parts without assembly. However, its large-scale adoption faces significant technical challenges such as warping and cracking, caused by thermal stresses during the manufacturing process. In this context, the Plastics Technology Centre (AIMPLAS) is leading the MAT3D-XL project, an initiative that seeks to address these limitations by developing sustainable composite materials and integrating auxiliary technologies into the printing process.
The project, funded by the Valencian Institute of Competitiveness and Innovation (IVACE+i) and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), seeks to improve large-format additive manufacturing with more sustainable materials and technologies that make the process more accurate and reliable.
MAT3D-XL focuses on the development of new recycled or bio-based thermoplastic materials reinforced with carbon, glass or natural fibers. These composites not only improve the strength and rigidity of parts but also promote the circular economy by reducing the use of non-renewable resources. In addition, the project incorporates auxiliary technologies such as infrared (IR) heating systems, which allow precise temperature control during printing. This improves adhesion between layers and reduces structural defects, increasing the reliability and final quality of the manufactured parts.
As highlighted by Daniel Rodríguez, an engineering researcher at AIMPLAS, "sustainability in additive manufacturing cannot be addressed solely through plastic recycling: it also involves redesigning materials to make them more stable during the manufacturing process and reducing waste from structural failures. For this reason, MAT3D-XL is committed to the development of composite materials which, through the addition of fibers (carbon, glass or natural), not only improve mechanical properties but also reduce thermal shrinkage, thereby reducing defects during the printing process."
Thanks to these innovations, he continued, “we can achieve more reliable prints, more reliable parts and less material waste. Moving towards this type of solution allows the sector to maintain high standards of technical performance, while promoting a realistic and efficient circular economy in large-format industrial applications.”
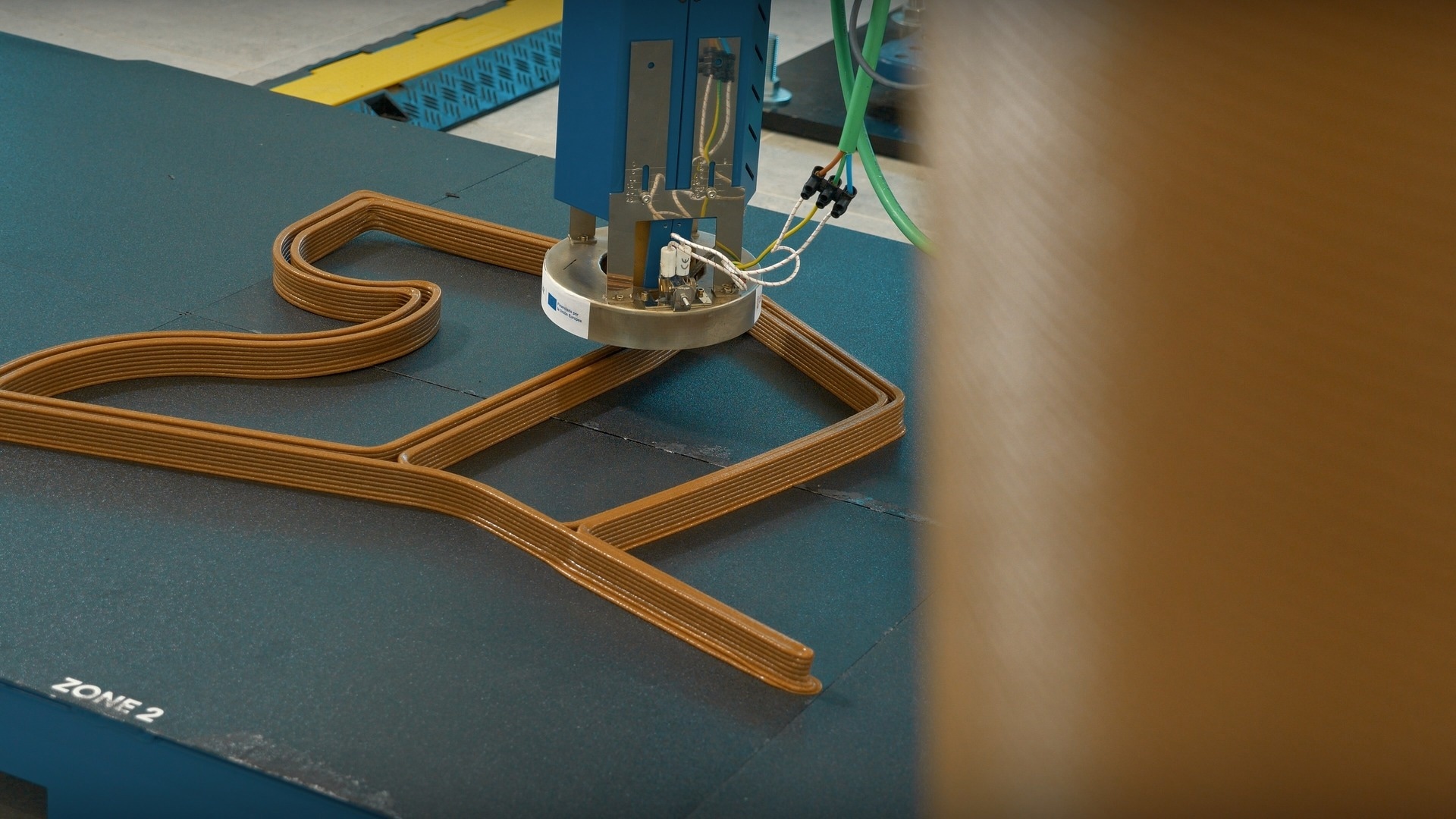
Image Credit: AIMPLAS
The possibility of manufacturing parts larger than one cubic meter without assembly opens new opportunities in sectors such as automotive, urban planning and interior design. AIMPLAS has developed several functional demonstrators that showcase the potential of the new materials and technologies applied. In collaboration with the company Plàstic Preciós La Safor, parts have been manufactured for street furniture benches, where the legs, printed in large-format additive manufacturing, are complemented by recycled shelves made by the company itself from plastic waste. In the field of interior design, a table has been developed with a tabletop manufactured by Plàstic Preciós and a single-piece base, with a slender geometry and more than one meter in height, produced using large-scale additive manufacturing. In addition, AIMPLAS has independently designed and manufactured an automotive spoiler, demonstrating the viability of using these materials in demanding applications.
All these demonstrators have been produced using new compounds developed as part of the project, formulated with recycled or bio-based pellets and reinforced with natural fibers, rice husks or recycled polymers, resulting in more sustainable parts with improved structural performance.
The MAT3D-XL project is part of the call for grants aimed at technology centers in the Valencian Community for R&D projects in collaboration with companies for the year 2024 by the Valencian Institute of Competitiveness and Innovation (IVACE+i), with funding from the ERDF.