Chitosan is found in abundance in organisms such as insects, crustaceans, and fungi, with shrimps being the main commercial source of the material. The process of manufacturing chitosan involves the deacetylation of chitin. This versatile polymer is highly sustainable, biocompatible, and biodegradable. Moreover, this abundant natural resource is cost-effective and non-toxic.
Chitosan can be functionalized by the addition of several functional groups via processes such as grafting and crosslinking. Additionally, this natural polymer can be incorporated into composite materials with other polymers and structural materials.
This natural resource can be retrieved from virgin sources as well as from agricultural, industrial, and food waste, which improves the circularity of the resource. The valorization of this organic polymer can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, waste, and costs in numerous industries. To date, several studies have focused on the use of chitosan for products in biomedicine, food, textiles, packaging, and agriculture. Several other innovative applications for chitosan are currently being researched.
Currently, there is a pressing need to move the world from a linear to a circular economy, where waste streams are used to produce value-added products for multiple industries. Recovering and reusing chitosan and other biopolymers will help to realize the aims of the circular economy.
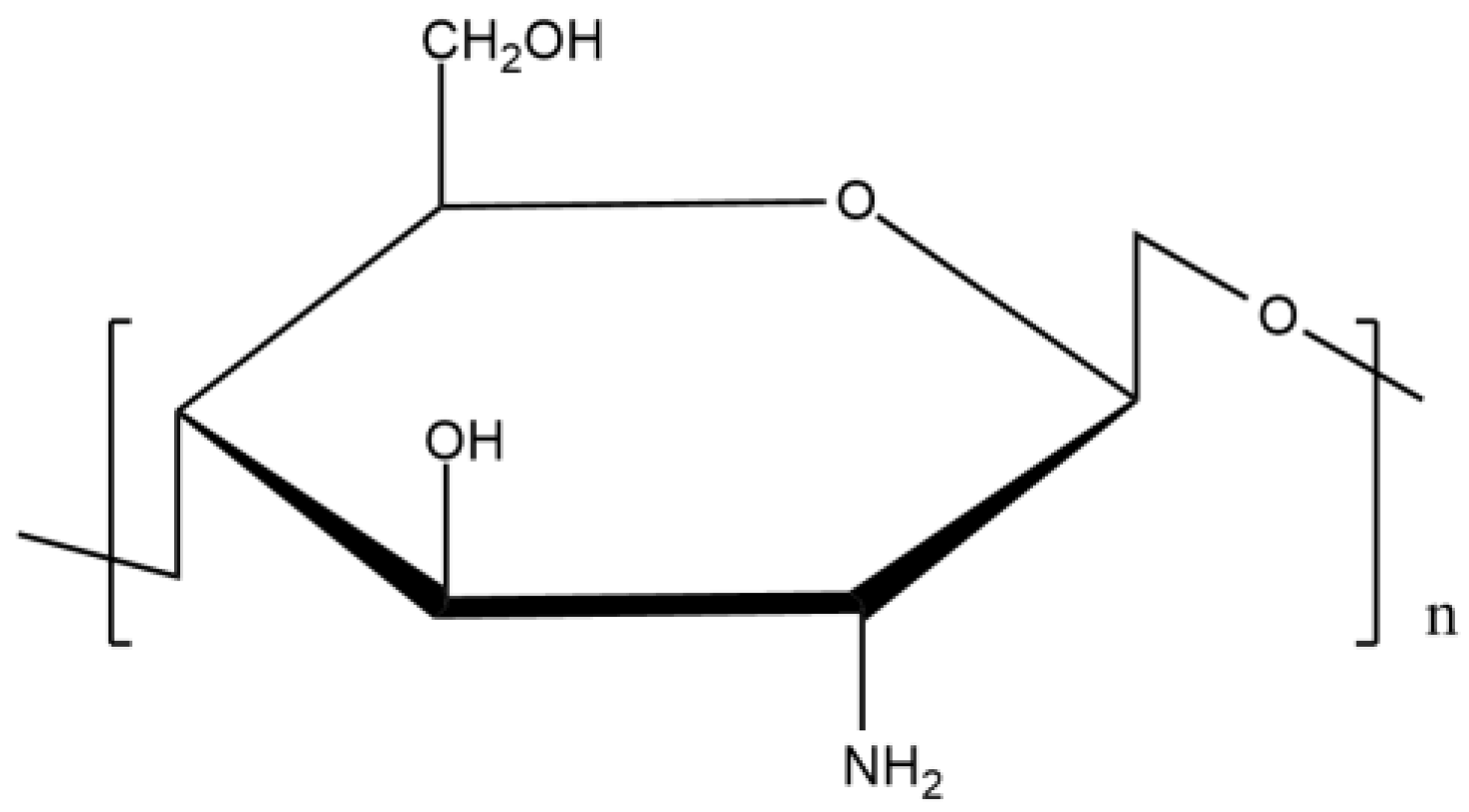
Chemical structure of chitosan. Image Credit: Maliki, S et al., Polymers
The Review
The mini-review has provided a perspective on how chitosan use can improve the sustainability and circularity of modern industry. The authors have provided a comprehensive literature review of nearly 250 studies, articles, and reviews from the past few decades covering a multitude of industries and research questions. Several novel and innovative applications of this versatile natural polymer have been discussed in-depth in the mini-review.
Commercial Applications of Chitosan
The biodegradability and non-toxic nature of chitosan are two of the main factors that have focused the attention of researchers on this sustainable, eco-friendly polymer. Its abundance overcomes issues with other raw materials, which may be limited. Its biocompatibility can be limited by low solubility in organic solvents, but this can be modified by chemical means. The structure of chitosan can be tailored for multiple applications.
Chitosan has been used in the wastewater treatment industry due to its absorbent properties, which makes it suitable for the removal of contaminants such as heavy metals and inorganic ions from water supplies. Heavy metals are particularly problematic because their bioavailability means that they can easily be absorbed by marine organisms and enter the food chain.
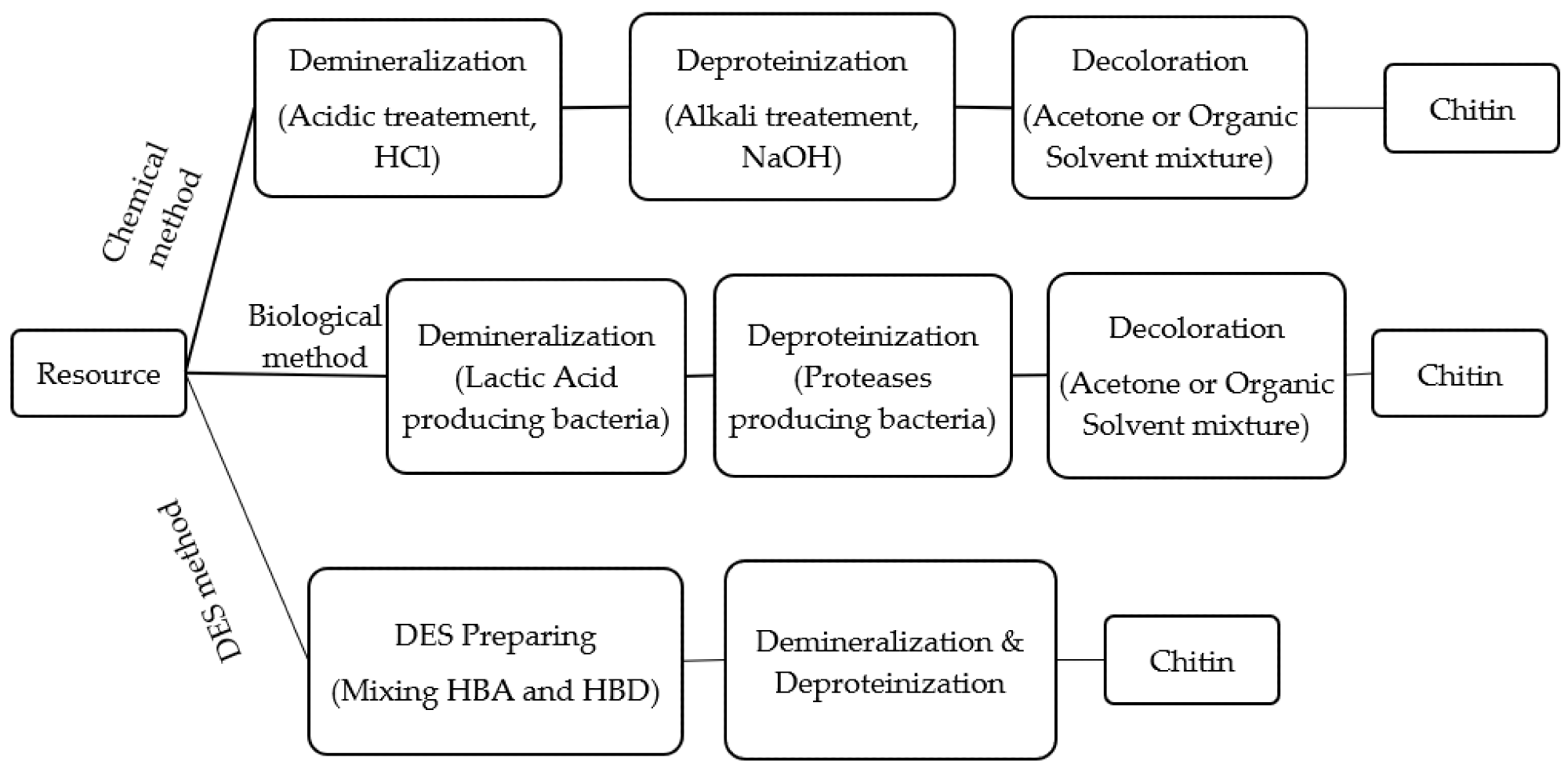
Extraction of chitin. DES: deep eutectic solvents; HBA: hydrogen bond acceptor; HBD: hydrogen bond donor. Image Credit: Maliki, S et al., Polymers
This material has also been explored for use as sustainable fertilizer additives and other agricultural applications such as seed coatings and can act as an antimicrobial and antifungal agent for use in more ecologically friendly pesticides.
Another application that takes advantage of chitosan’s antimicrobial properties is advanced food packaging, which improves the quality and shelf-life of food. Preparing hybrid materials with chitosan can facilitate the production of films with selective permeability based on the requirements of the packaging. Chitosan has also been investigated for use in food additives, functional ingredients, and to improve the dietary fiber content of foodstuffs.
Another important industry that has explored the application of chitosan and hybrid materials is the biomedical industry. Uses investigated for this remarkable polymer include drug delivery, membranes, and as scaffold materials for applications such as tissue engineering. Furthermore, chitosan has been evaluated for use in personal care products, green chemistry, and the paper industry.
Sustainable Production of Chitosan
Whilst the most common commercial sources of chitosan come from crustaceans such as shrimps, the production route is not sustainable. Production of shellfish is a resource-intensive process. For this reason, there has been an increased research focus in recent years on other sources. Various production routes for recovering chitosan from fungal and microbial biomass have been investigated by researchers, with favorable advantages over conventional production processes.
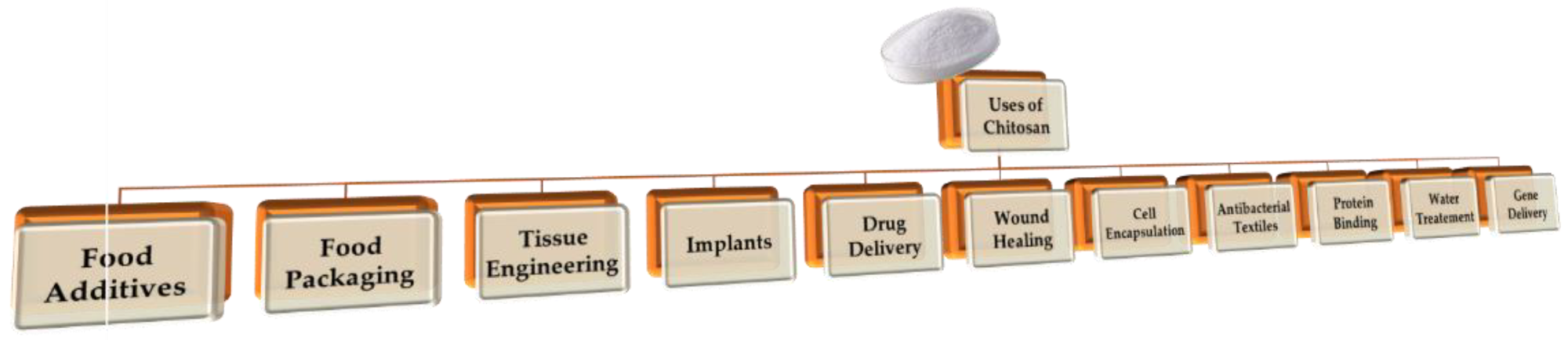
Different uses of chitosan. Image Credit: Maliki, S et al., Polymers
Another key issue with chitosan production is the use of harsh reagents such as bases and acids. Aside from not being sustainable, the use of these reagents can damage the structure of chitosan. Recent developments in sustainable production have involved the use of natural eutectic solvents and using microorganisms to extract chitin. Developing more sustainable extraction processes also overcomes issues with polluted wastewater, which can cause vast environmental damage if not treated.
The Future
The mini-review has stated that the use of chitosan will likely increase in the future, replacing many conventional materials used in numerous industries. Research is currently addressing challenges with the material’s properties, reducing the use of hazardous solvents, and reducing energy consumption. This material has the potential to replace many key commercial materials and improve the sustainability and circularity of multiple industries.
Further Reading
Maliki, S et al. (2022) Chitosan as a Tool for Sustainable Development: A Mini Review [online] Polymers 14(7) 1475 | mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/14/7/1475
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.