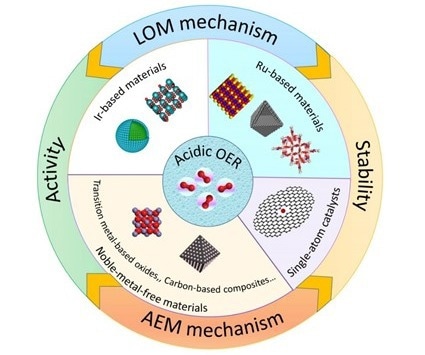
The classification and the relationship between activity/stability of acidic OER electrocatalysts. Image Credit: NIMTE
Proton exchange membrane (PEM)-based water electrolysis provides specific benefits over alkaline water electrolysis, including compact design, quick response, high voltage efficiency, and high gas purity. The advancement of PEM-based water electrolysis is still hampered by the acidic OER electrocatalysts’ low stability, limited efficiency, and high cost.
Researchers at NIMTE have thoroughly analyzed, organized, and discussed the recently reported acidic OER electrocatalysts in terms of elements based on earlier studies on electrocatalysts for OER.
According to the origin of oxygen atoms, a significant emphasis was placed on the OER processes, which can be divided into two categories: the adsorbate evolution mechanism and the lattice oxygen oxidation mechanism.
It was clearly outlined how acidic OER electrocatalyst activity and stability relate to one another. The researchers also suggested a stability test strategy to assess the loss of intrinsic activity.
Acidic OER electrocatalysts’ current development difficulties and unresolved problems, such as the usage of carbon-based materials, were reviewed. Also, ideas for the production of highly effective acidic OER electrocatalysts for PEM-based water electrolysis were provided.
The Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the K. C. Wong Education Foundation, Ningbo, the “From 0 to 1” Innovative initiative of CAS, etc. provided funding for this project.
Journal Reference
Lin, Y., et al. (2022) Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Acidic Media. Advanced Materials. doi:10.1002/adma.202210565.