Nov 2 2017
Polymers are highly valued by industry and progressively used as substitutes for metals in the manufacture of automobile parts, firearms, and others. Such parts are marked with serial numbers, for traceability and security purposes.
 Recovering erased serial numbers in a polymer Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society
Recovering erased serial numbers in a polymer Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society
The numbers may however be partially or totally erased, and although there are methods for recovering them from metal parts, there is no method so far for polymers, but that could soon change. In an article published in Analytical Chemistry, researchers have shown the potential of a non-destructive technique for making abraded serial numbers on polymers discernible again.
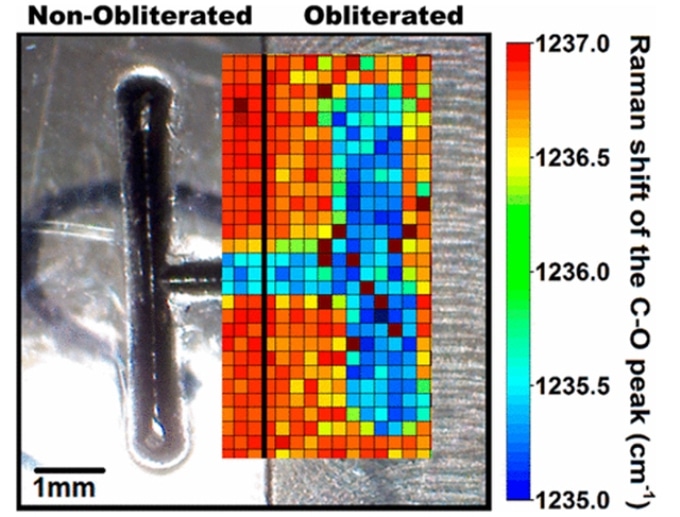
Cédric Parisien, an INRS master’s student in energy science and materials, used Raman spectroscopy to reconstruct deleted information from a sample of polycarbonate, a polymer that is widely used in the manufacture of bulletproof products. The method could be of significant advantage to forensics, since it needs no pre-treatment and does not deform the sample.
The stamping technique used to engrave serial numbers creates deformations deep in the material, we used Raman spectroscopy to reveal those changes and get a kind of fingerprint for use in recovering erased images, without recourse to thermal, chemical, or other treatments.
Andreas Ruediger, INRS professor and study coauthor
Other studies are in progress to verify the reliability of this new technique on a range of other polymers and materials such as ceramics for both quality control and security applications.