In recent years, additive manufacturing is growing in popularity with capabilities beyond traditional manufacturing, but limitations of the raw material have hindered the widespread adoption of 3D printing.
Image Credit: Shutterstock/ nikkytok
ALD has been used to tackle limitations like flowability, alloy type and oxidation resistance and demonstrations have exhibited stronger final parts, enhanced processing capabilities and lower costs.
Reduced Cost
Using ALD to better powder properties can decrease costs by removing unnecessary processing steps. The cost of Tungsten powder is one example and it is usually in the range of $30 per kg and needs plasma spheroidization for successful flowability and printing, which increases the cost of the powder by 10x.
By using ALD instead of costly procedures such as plasma to enhance flowability, the cost of Tungsten powder can stay low.
Processing Enhancements
Forge Nano has shown improvements to rheological properties of powders like oxidation protection, flowability, dispersion, bed density, crystallinity, corrosion resistance and shelf life, which have allowed enhanced homogeneity and reproducibility of parts, use of nanomaterials and new alloy opportunities.
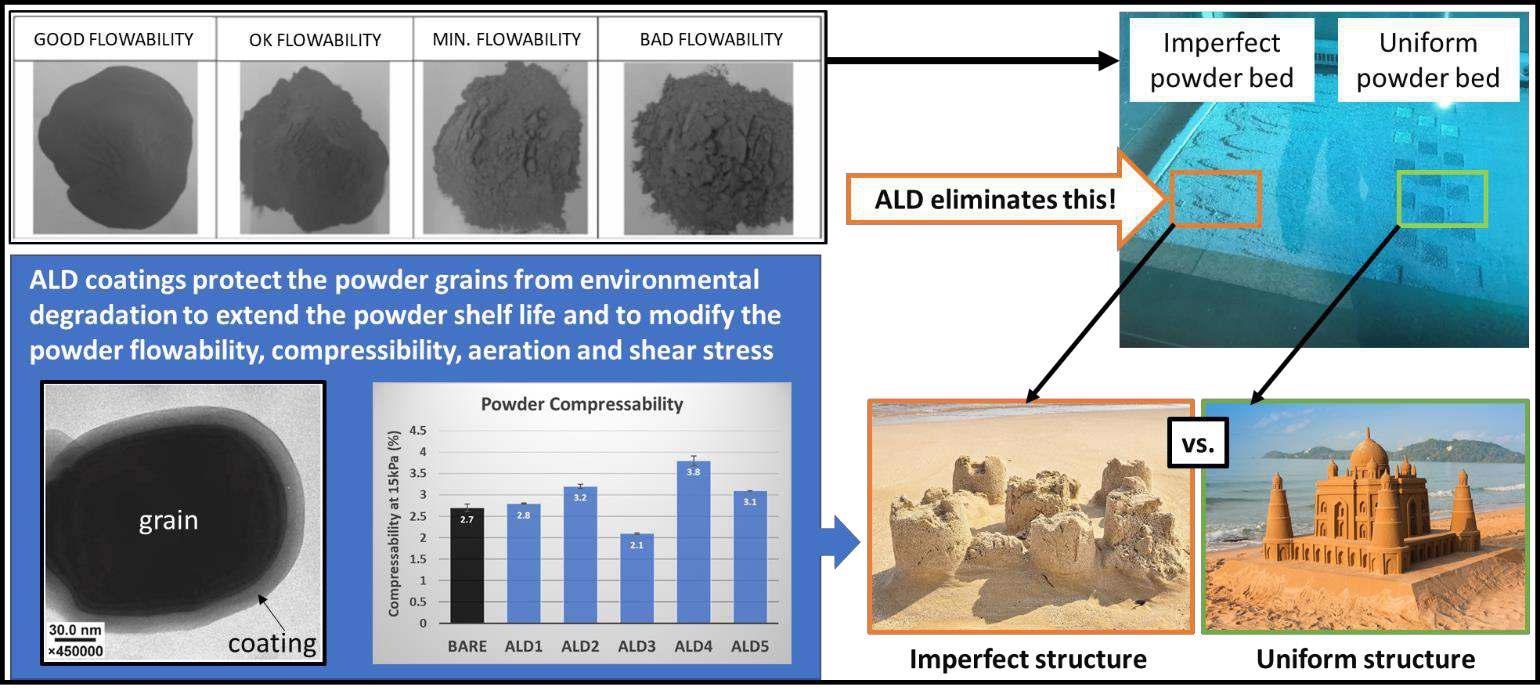
Image Credit: Forge Nano
Parts Improvements
ALD can enhance mechanical properties like elongation, strength and flexibility of printed parts via the introduction of nucleants, or controlled nucleation sites, which change the grain growth behavior during additive manufacturing printing enabling better electrical properties, mechanical properties and more.
Forge Nano has a vast array of knowledge in scaling ALD with the largest ALD capabilities in the world.
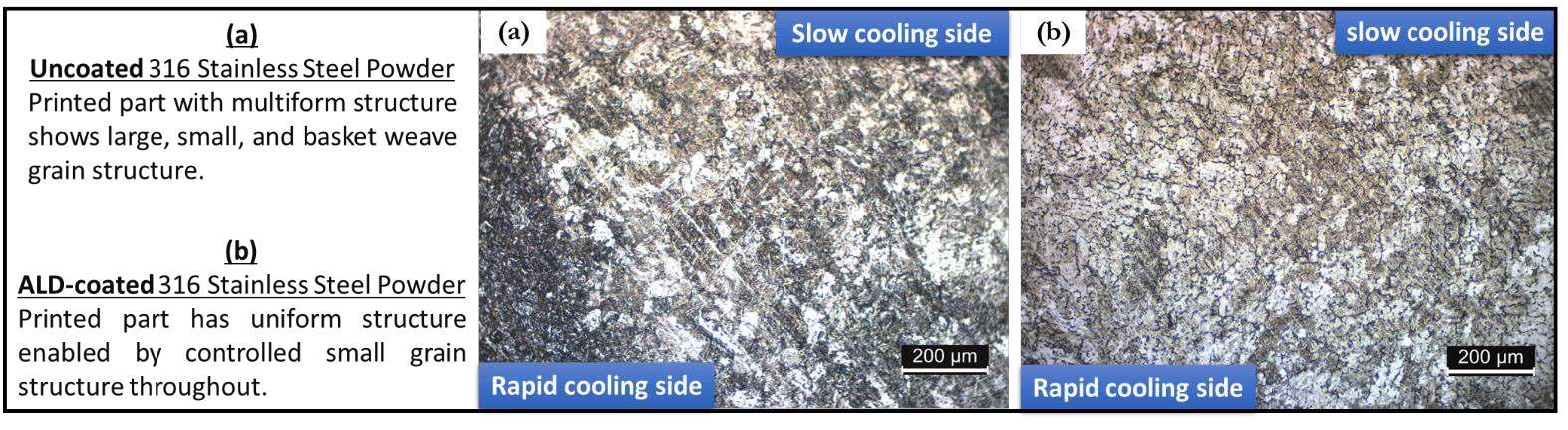

Image Credit: Forge Nano

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Forge Nano.
For more information on this source, please visit Forge Nano.