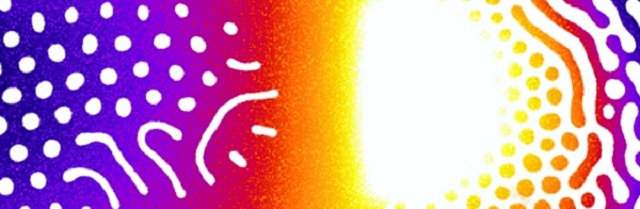
 Thermographic image of an integrated circuit taken with pyro-magnetic-optics. The image shows the magnetic domains as well as heat distribution along the wires. The warmest point (yellow to white) indicates that the wires are close to each other in a confined place. Temperatures differ about 0.5 to 1 degree Celsius. (Credit: McCord)
Thermographic image of an integrated circuit taken with pyro-magnetic-optics. The image shows the magnetic domains as well as heat distribution along the wires. The warmest point (yellow to white) indicates that the wires are close to each other in a confined place. Temperatures differ about 0.5 to 1 degree Celsius. (Credit: McCord)
A new technology developed by Kiel University scientists allows visual identification of even minute temperature differences at high spatial resolution, irrespective of the material. This novel concept reported in the current edition of Advanced Materials journal, challenges other similar procedures.
The most popular yellow to blue thermal images are often deployed so that weak spots can be visually identified through infra-red measurements at the time of renovating houses or trying to make them more energy-efficient. Thermographic imaging is also one of the commonly used materials testing techniques. However, the technique can lead to large measurement errors based on the material.
Kiel scientists, have exploited the magnetic properties of a specific material. Instead of a thin, transparent layer of a garnet compound, the scientists placed an integrated circuit of a microchip on the object to be studied. The material layer responded to even the slightest temperature changes in the circuit by changing its magnetic properties. As the temperature of the material increased, its magnetization was reduced.
Using a polarization microscope, the magnetization that differs based on the temperature can be viewed. The polarized light in the microscope is directed along a particular oscillation direction. The light is reflected in a different manner based on the materials’ magnetization, once it approaches the thin layer surface. The reflected light is then captured using a digital, light-sensitive camera. The temperature distribution in the circuit and the small magnetic domains of the material can be observed in the magneto-optical images. These are individual regions with similar polarization.
The new material developed by the scientists serves as an accurate temperature meter. Even minimal changes of up to one hundredth of a degree Celsius taking place in milliseconds with a micrometer resolution can be displayed through this novel technique. Professor Jeffrey McCord, head of the study at the Kiel Institute for Materials Science, is positive that "Our technology therefore opens up brand new possibilities for different thermographic imaging applications." It is possible to conceive new thermographic camera models. The new technique named “Pyro-Magnetic-Optics” could result in more precise and easier error analysis of electronic components.
The research work was carried along with the scientists from the Russian Tver State University and the Russian Research Institute for Materials Science and Technology.
References