With the rise of innovative technologies, several important industrial sectors have undergone a rapid and fundamental transformation. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a key emerging technology that connects the physical and virtual worlds through a network of internet-connected devices that can communicate with each other without the need for human interaction.
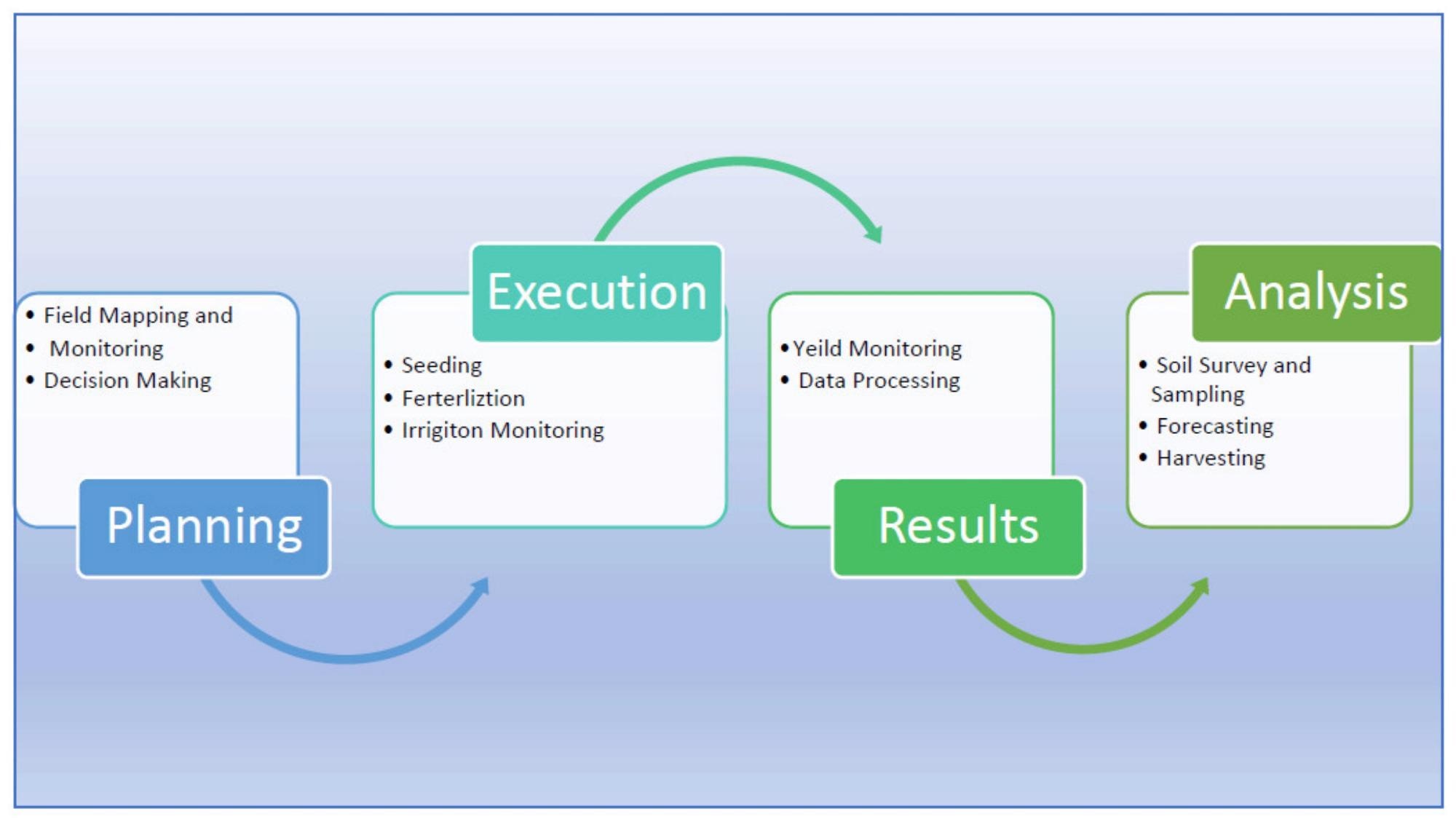
Smart precision agriculture cycle. Image Credit: Rehman, A et al., Agrnomies
IoT devices confer several advantages for industry, including automation, control, real-time information access, improved monitoring using sensors, machine-machine communication, cost reduction, and the use of big data for predictive analysis. Examples of IoT applications include smart homes, smart energy devices, connected vehicles, and smart agriculture.
The IoT market has grown rapidly over recent years as well. In 2019, it was worth $690 billion and is predicted to reach $1256.1 billion by 2025. This represents a global compound annual growth rate of 10.53% between 2020 and 2025. The IoT market is making significant inroads into numerous sectors of industry and society.
Using IoT in Smart Agriculture
As the world population has grown, so has the need for secure food supplies and improved agricultural practices. Increasing demand for better quality and larger quantities of food has led to the rapid modernization of the industry, with advances in technology, infrastructure, and improved growing methods being developed in recent decades. The Internet of Things provides promising applications for the modern agricultural sector.
The demands on the agricultural industry are pressing. The world’s population is projected to reach 10.1 billion people by 2050, leading to increased demand for land space to be given over to growing crops and rearing livestock. By 2050, there will need to be a 70% growth in food production. Additionally, commercially important non-food crops such as cotton and gum are in increasing demand, alongside traditional food crops which are increasingly being utilized for biofuel production.
The challenges of the 21st century have facilitated the need for smart agriculture. Climate change, increasing instances of extreme weather events, population growth, and soil degradation all affect the viability of crops and the need to increase yields. Solutions are needed if timely and regular agricultural growth is to be assured. Crop protection, yield projection, and land appraisal are essential elements of world food production and security.
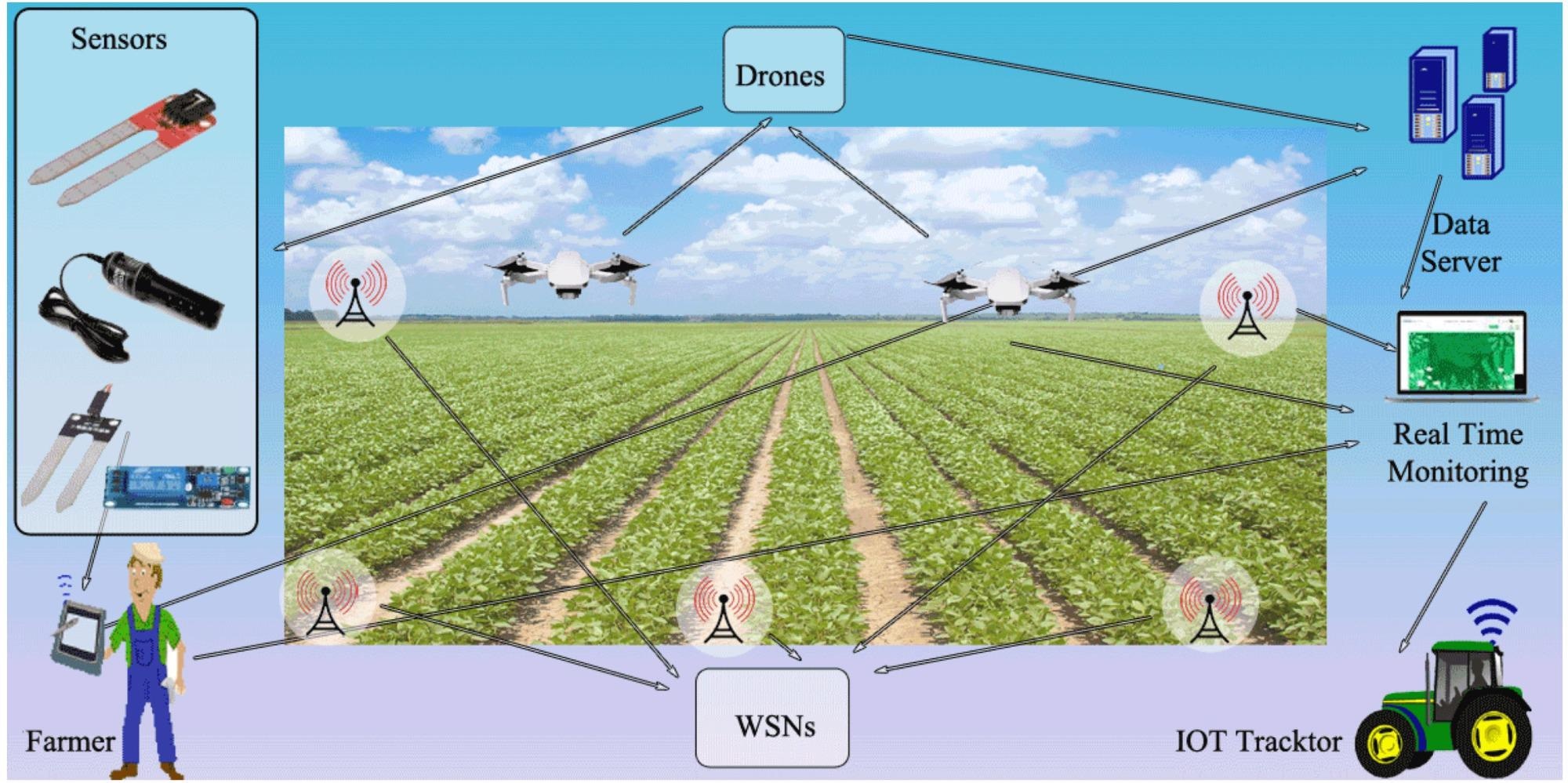
IOT-based smart agriculture monitoring system. Image Credit: Rehman, A et al., Agrnomies
The paper published in Agronomy has investigated the potential of IoT technologies to become a central technology in the move toward smart agriculture in the 21st century. Examples of IoT applications in agriculture include farm management, greenhouse environmental control, animal and herd monitoring, emissions monitoring, irrigation control, farm management systems, autonomous machinery, and drones.
Farmers can monitor field conditions in real-time using a network of internet-connected smart sensors and mobile devices, leading to improved regulation. Data can be analyzed to predict crop yields with increased precision, saving cost and improving the overall efficiency of farm operations. Diseases, pesticides, and irrigation monitoring can be improved with IoT technologies. Smart, connected devices are increasingly being employed across the entire agricultural chain from sowing to the transportation of products.
Furthermore, autonomous equipment is becoming commonplace in contemporary farming. Drones, combine harvesters, tractors, robots, and satellites are increasingly being utilized, improving the efficiency of harvesting, storage, monitoring, and other agricultural activities. Data collected onsite by smart sensor technology can be fed back to central hubs and analyzed to improve future operations.
Contributions of the Study
The authors behind the study published in Agronomics have sought to make a significant contribution to the field of smart agriculture and provide an overview of the current state of IoT implementation and future directions for the agriculture industry. The study has examined key effective features, smart IoT-connected agriculture equipment, and technologies, and current barriers, problems, and possibilities for the field.
Additionally, the study has contributed to current knowledge of the area, including current expectations of the agriculture industry, based on the contribution of IoT technologies in solving the problems faced by the sector. Numerous application fields have been identified. Current literature has been summarized by the authors. Furthermore, the authors have stated that the research will be expanded on in the future to include privacy and security issues.
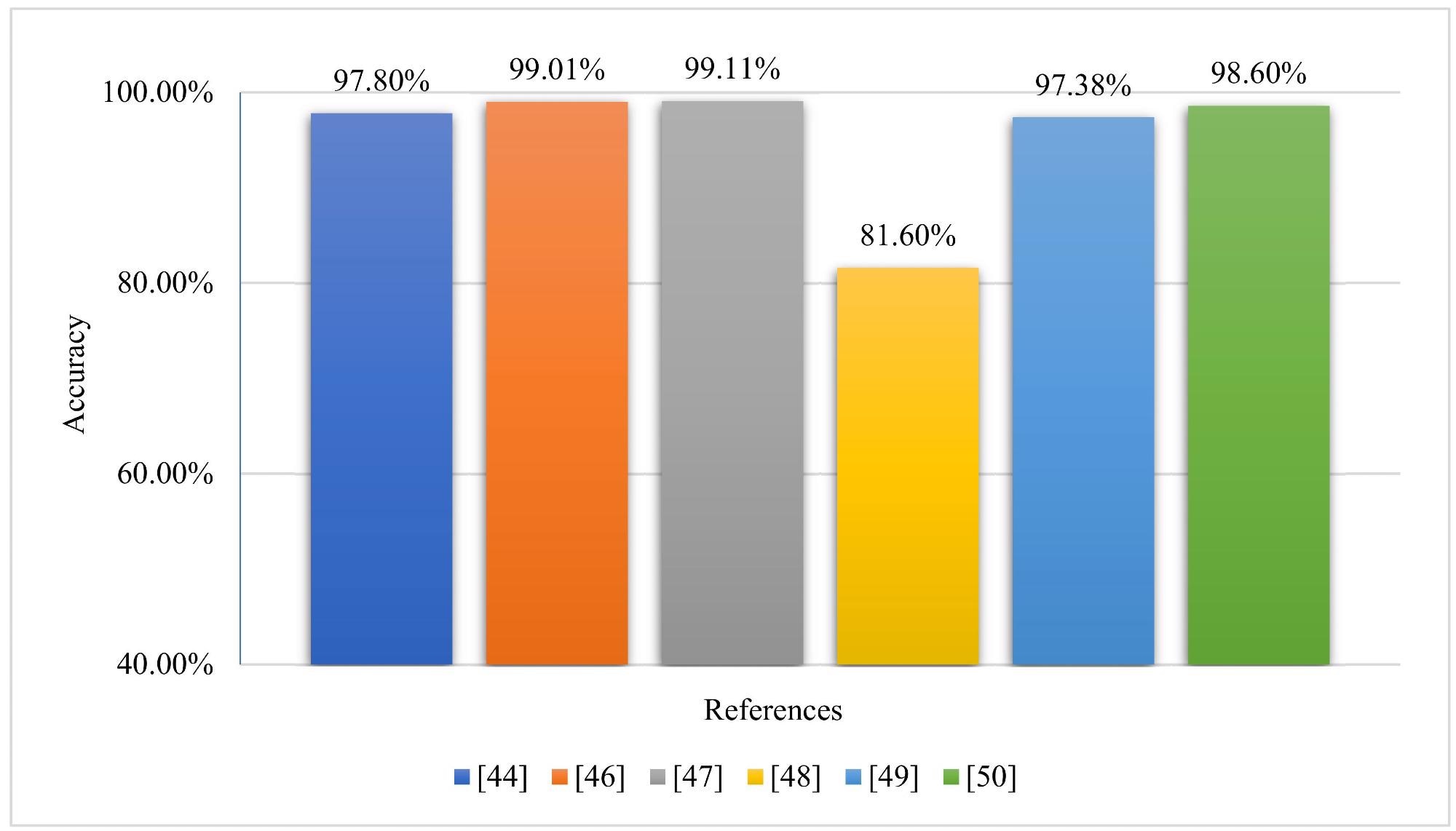
Accuracy-based analysis of the different state of the art techniques. Image Credit: Rehman, A et al., Agrnomies
The Future
The pressing need to increase agricultural production to feed a growing world population has facilitated the need for technological development. Traditional farming techniques are increasingly becoming unfit for purpose. IoT technologies including autonomous equipment, wireless communication technologies, and smart sensors are playing a key role in the development of smart agriculture. Agriculture must change to keep pace with the demands of the 21st century if food security is to be maintained.
Further Reading
Rehman, A et al. (2022) A Revisit of Internet of Things Technologies for Monitoring and Control Strategies in Smart Agriculture [online] Agronomics 12(1) | mdpi.com. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4395/12/1/127
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.