A new hydrogen fuel cell has been developed by scientists at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST). The fuel cell is not just considered to be the long-standing one developed in the world so far but is also highly affordable.
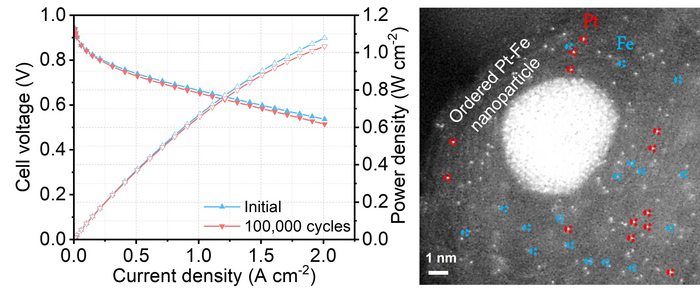 (Left) The new hybrid catalyst maintains the platinum catalytic activity at 97% after 100,000 cycles of accelerated stress test; (Right) The new electrocatalyst contains atomically dispersed platinum, iron single atoms and platinum-iron nanoparticles. Image Credit: Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
(Left) The new hybrid catalyst maintains the platinum catalytic activity at 97% after 100,000 cycles of accelerated stress test; (Right) The new electrocatalyst contains atomically dispersed platinum, iron single atoms and platinum-iron nanoparticles. Image Credit: Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
This breakthrough could set the stage for an extensive application of green energy in the pursuit of a carbon-neutral world.
A hydrogen fuel cell is a hopeful clean energy option as it produces power by transforming oxygen and hydrogen into electricity, with zero-emission of carbon dioxide, particulate matter, and other air pollutants that might result in smog and other health issues.
Regardless of its environmental advantages and years of development, the hydrogen fuel cell was still not commercialized in an extensive manner. This is because the electrocatalyst, which is primarily made of the pricey and rare metal platinum, is crucial to the device’s ability to generate electricity.
Researchers have made an attempt to come up with alternatives by substituting platinum with highly common and low-cost materials like iron–nitrogen–carbon. However, those materials have either proven ineffective in power generation or exhibit poor durability.
At present, a research group headed by Professor Minhua Shao from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering at HKUST has discovered a new formula that could not only reduce the proportion of platinum utilized by 80% but, it also set a record regarding the durability level of the cell.
Despite using only a low portion of platinum, the new hybrid catalyst was regulated to retain the catalytic activity of the platinum at 97% following 100,000 cycles of an expedited stress test, in comparison to the present catalyst which generally absorbs a drop of more than 50% in performance after 30,000 cycles.
In another test that was conducted, the new fuel cell did not exhibit any performance decay following operating for almost 200 hours.
One cause behind such excellent performance was the truth that the new catalyst consists of three various active sites for the reaction, rather than just one in present catalysts.
Utilizing a formula consisting of atomically dispersed platinum, iron single atoms, and platinum–iron nanoparticles, the new mix expedites the reaction rate and obtains a catalytic activity that is 3.7 times greater compared to the platinum itself. On a theoretical basis, the higher the catalytic activity, the greater the power it offers.
Hydrogen fuel cell is an energy conversion device essential for our aspiration of achieving a carbon neutral world, there is a need to expand its use amidst our fight against climate change.
Minhua Shao, Professor, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Shao added, “We are delighted to see our research findings bringing this goal a step closer. Thanks to the Government’s Green Tech Fund, we will seek to further refine the catalyst and make it compatible with fuel cell vehicles and other electrochemical devices.”
Shao is also the Director of HKUST Energy Institute.
Financial support for the study was offered by the National Key R&D Program of China, Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee, and the Research Grant Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region.
Journal Reference:
Xiao, F., et al. (2022) Atomically dispersed Pt and Fe sites and Pt–Fe nanoparticles for durable proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature Catalysis. doi.org/10.1038/s41929-022-00796-1.