Although the classical methods have been successful in NP production, their disadvantages, especially the toxic by-products and expensive equipment and components, have always been a major concern.
This latest study has solved all such problems efficiently. Nanoparticles were efficiently synthesized and their physical and chemical properties and reactivities were validated thoroughly. The study has also been successful in proving the biocompatibility of these particles. Hence, the suitability of ZnONPs for biomedical applications and clinical development has been proved efficiently.
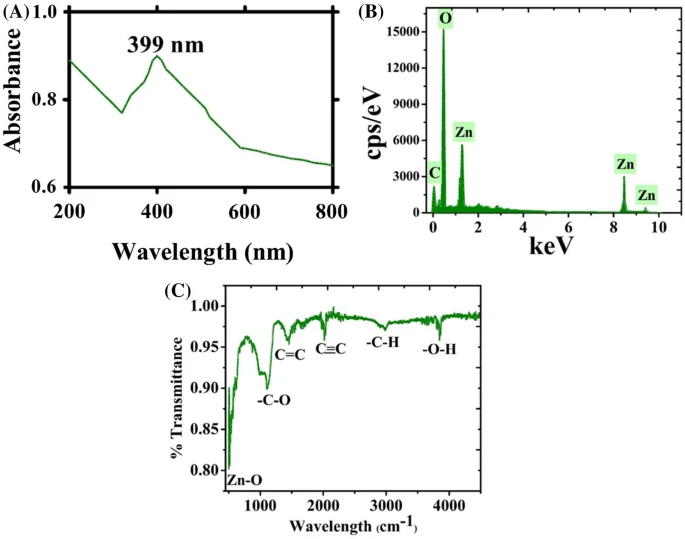
Figure 1. (a) UV visible spectroscopy, EDX and FTIR analysis of ZnONPs (a) UV; (b) EDX; (c) FTIR.
Zinc Oxides Nanoparticles and Elaeagnus Angustifolia L.
Although the classical methods have successfully resulted in the synthesis of nanoparticles, costs and toxic emissions have been forcing researchers to search for new environment-friendly methods.
Zinc oxide nanoparticles have been identified as a very suitable type of nanoparticle, and have been successfully utilized in various industries such as ointments, adhesives, dyes, pottery manufacturing, and various ceramic production industries.
The biomedical applications include antioxidant and antileishmanial applications, as well as integration in various products owing to biomedical compatibility.
The Elaeagnus Angustifolia L. is a distinct nitrogen-fixing thorny plant with various phytochemical constituents such as sugars, caffeic, vitamins and sugar minerals, etc. Its extract is very useful for users as a pain inhibitor as well as having use fighting infections and diseases such as arthritis and jaundice etc. All such characteristics make such materials an automatic choice for nanoparticle production.
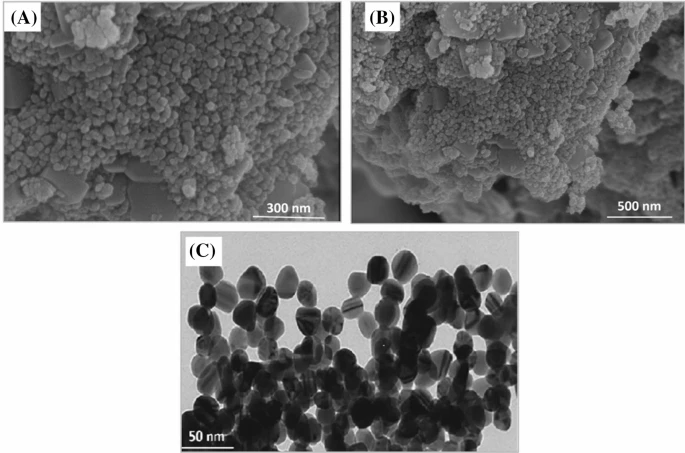
(a, b) SEM analysis of biogenic ZnONPs (c) TEM analysis of biogenic ZnONPs. Image Credit: Iqbal, J. et al., Scientific Reports
Methods and Materials
The latest study in Scientific Reports implemented property determination and validation processes all while following ethical and pre-determined guidelines. The plant was collected from Parachinar, Pakistan, and washed with deionized water, dried, and stored in an airtight bottle for implementation during the study.
The synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles occurred according to the standards defined by mixing 1g of Zinc-nitrate hexahydrate with 100mL of the leaf extract. Just like the synthesis process, other relevant procedures were also performed such as the thorough analysis of biocompatibility potentials, validation of enzyme inhibition, testing of antibacterial activities, validating anti-fungal actions as well as the anticancer and antileishmanial potential detection of the nanoparticles.
All such processes were carefully performed, along with validation of results and properties with published literature to obtain the accurate properties and synthesize environmentally-friendly ZnONPs that are highly advantageous for biomedical applications.
Results and Findings of the Latest ZnO NP Green Synthesis Research
The study in Scientific Reports revealed that the color of the solution of the parent mixture of Zinc nitrate hexahydrate with the leaf extract changed its appearance from light brown to yellowish black.
This is a confirmation of the reduction process that takes place, which converts Zinc ions to Zinc oxide nanoparticles. The bioactive compound detection and analysis were done via FT-IR analysis, and biomolecule identification was successfully done by spectroscopic technique.
Scanning Electron Microscopic analysis confirmed that spherical shaped ZnO nanoparticles were obtained, whose size was estimated to be about 26 nm via the Scherrer’s equation. The next important step was the confirmation of biomedical compatibility.
A test was performed to evaluate the hemolytic property by exposing erythrocytes to ZnONPs. The test results showed a 27.38% hemoglobin release at the highest dose of 100 µg mL−1. This value is the consolidated proof of the biosafety, non-toxicity, and compatibility of the ZnO nanoparticles.
This further test successfully indicated the enzyme’s inhibition capability, antibacterial and antifungal properties, antioxidant, anticancer as well as the Antileishmanial potential of the nanoparticles, successfully declaring them the most suitable product synthesized.
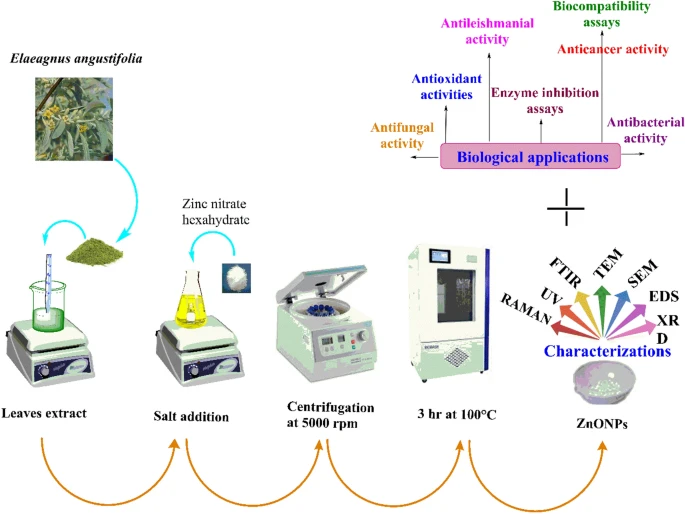
Study scheme depicting synthesis, characterization and biological applications of ZnONPs. Image Credit: Iqbal, J. et al., Scientific Reports
This study truly has revolutionized the nanoparticle synthesis procedure. The ecofriendly, cost-effective, and antitoxic process could soon be widely utilized for anticancer, nanoparticle synthesis as well as biomedical applications. The leaf extract has distinct anti-toxic characteristics which make the NP safe and biocompatible.
The study has successfully identified various biomedical applications of such nanoparticles as well as depicting the dose-dependent operational behavior of such particles. Hence, it is safe to say that the particles are safe for biomedical applications and other processes where microbial growth is to be inhibited.
More biological, as well as laboratory mechanistic research in various animal models, is required in the future to assess their biosafety relevance in numerous bioactive metabolites.
References
Iqbal, J., Abbasi, B. A., Yaseen, T., Zahra, S. A., Shahbaz, A., Shah, A. S., . . . Ahmad, P. (2021). Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Elaeagnus angustifolia L. leaf extracts and their multiple in vitro biological applications. Scientific Reports. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-99839-z
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.