Raman spectroscopy is a highly regarded technique known for its remarkable chemical sensitivity in identifying various solid and liquid samples. However, due to gases' diffuse characteristics, analysis via this naturally weak optical scattering technique presents a challenge.
An effective approach to address this issue is to lengthen the optical path, enhancing the interaction between excitation photons and the Raman scattering centers. This adjustment increases the production of distinct energy-shifted Raman photons, which provide the unique chemical fingerprint of the target gas or gases.
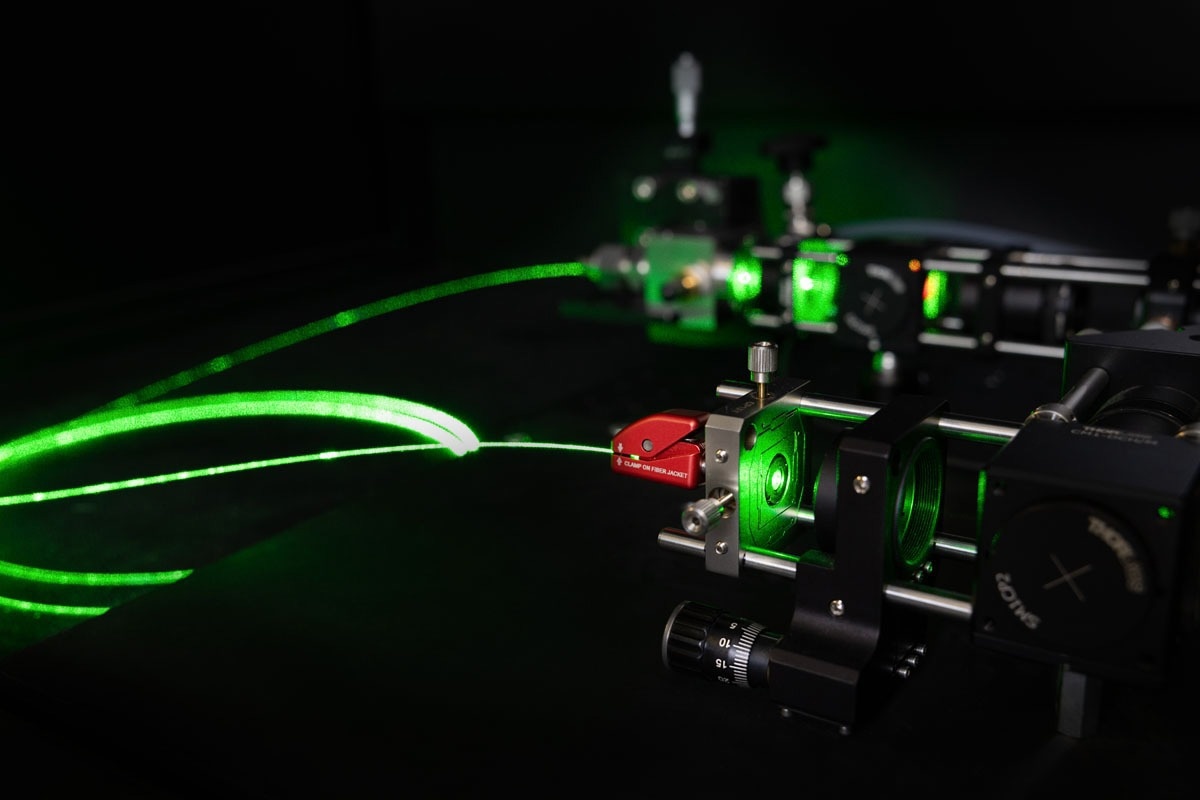
Image Credit: IS Instruments
Product Specifications
Gas Raman
ISI’s gas Raman instrument employs hollow-core micro-structured optical fibre (HCF) technology, allowing the target gas species to be drawn into the internal volume of the HCF.
The Raman spectra of the gas are recorded through a hardware setup that includes a laser, a dispersive spectrometer, and coupling optics. This instrument provides rapid in-situ gas measurements and offers numerous advantages over conventional gas chromatography or Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) methods.
Gas chromatography (GC) is typically the most widely used technique for gas phase metrology. However, gas chromatographs have various limitations, such as high costs and the necessity for a skilled technician to manage the system and analyze the results.
In GC, samples cannot be measured in situ, necessitating off-line analysis, which prolongs the measurement cycle. GC also requires a preemptive column tailored to the gases the operator anticipates encountering. IS Instruments’ gas Raman system effectively resolves these issues.
Specifications
Source: IS Instruments
| Feature |
Detail |
| Raman operating λ |
532 nm |
| Configuration |
Hollow core fibre (HCF) |
| Operating Range |
400-4500 cm-1 |
| Resolution |
<4 cm-1 |
| Detector |
Andor iVac 316 |
| Fiber coupled |
SMA or FC/PC |
| Dimensions |
Tabletop |
Key Features/ Benefits
- In-situ measurements that decrease the duration of the metrology cycle
- No need to halt pipelines for sample collection
- Non-technical workers can operate the system
- Multiple-channel gas detection capabilities
- No requirement for a predictive column based on anticipated results
Applications Include
- Manufacturing process monitoring
- Nuclear fusion
- Natural gas/ hydrogen blending
- Nuclear decommissioning
- Security and Defense
- Environmental monitoring